Figure 2.
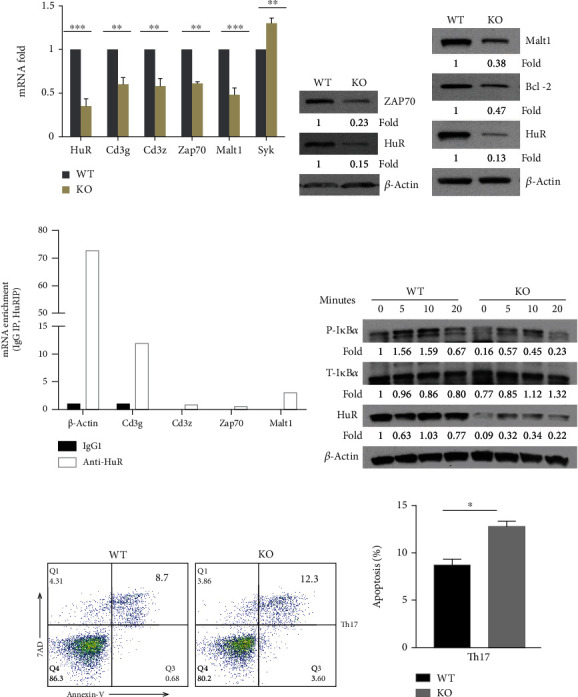
HuR modulates TCR/CD3 complex signaling in Th17 cells. Naïve CD4+ T cells from the spleen of WT and HuR KO mice were isolated and cultured under Th17 cell polarization conditions as described in Materials and Methods. The polarized cells were collected for further experiments at 4-5 days after culture. (a) Total RNAs were extracted and reversely transcribed into cDNA. The mRNA levels were analyzed by RT-qPCR. (b, c) Knockout of HuR decreased Zap70, Malt1, and Bcl-2 abundances detected by western blot assay. (d) RIP assay was performed to determine if CD3g, Zap70, and Malt1 mRNAs were associated with HuR protein in Th17 cells. One representative experiment result is known here. The repeated RIP experiment also got the same tendency of results. (e) Naive WT and HuR KO CD4+ T cells were cultured at Th17 cell polarization condition for 3 days. Then, Th17 cells were rested 2 days in the presence of IL-2 (3 ng/ml) following restimulation by Th17 cell-polarizing cytokines (TGF-β+IL-6) without IL-23 for the indicated times. The level of phosphorylated IκBα, but not total IκBα, was decreased in HuR KO CD4+ T cells compared to WT control cells at indicated time points. The levels of proteins were detected by western blot assay. (f) There is a little difference between HuR KO Th17 cells and WT Th17 cells susceptible for apoptosis as determined by flow cytometry assay. (g) Summary of three independent experiments was shown for apoptosis detected by flow cytometry analysis. Data in (a) represents the summary of three independent experiments (mean ± SEM). Student's t-test was used for statistics analysis. ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01. Data in (b)–(e) represents one of the three independent experiments.
