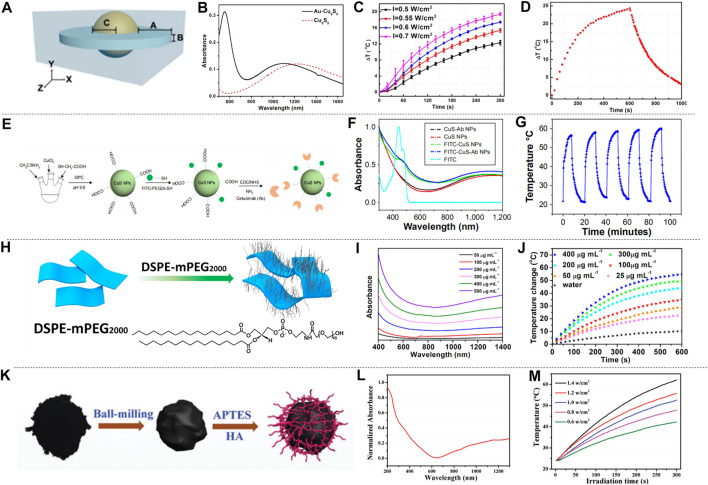
FIGURE 5.
Photothermal characteristics of metal sulfur oxides. (A) DDA simulation structure diagram of Au-Cu9S5 NPs. (B) The absorption spectrum of Au-Cu9S5 NPs. (C) Temperature characteristic curves of Au-Cu9S5 NPs solutions excited by 1,064 nm with different power densities. (D) Temperature change graph of Au-Cu9S5 NPs solution excited by 1,064 nm laser (reproduced from (Ding et al., 2014) with permission from American Chemical Society). (E) Synthesis of CuS-Ab NPs. (F) Absorption spectrum of CuS-Ab NPs. (G) The temperature change curve of the CuS-Ab NPs solution irradiated by a 1,064 nm laser for five cycles (reproduced from (Li et al., 2018) with permission from Dove Medical Press LTD.). (H) Schematic diagram of DSPE-mPEG wrapped TONW NRs. (I) Absorption spectra of different concentrations of PEG-TONW NRs solutions. (J) The temperature rise curve of PEG-TONW NRs solution with different concentrations irradiated by a 1,064 nm laser (reproduced from (Cheng et al., 2019) with permission from American Chemical Society). (K) Titanium dioxide synthesis diagram. (L) Absorption spectrum of Ti2O3 NPs. (M) Temperature-time graphs of Ti2O3 NPs irradiated by 1,064 nm lasers with different power densities (reproduced from (Zeng et al., 2018) with permission from Royal Society of Chemistry).