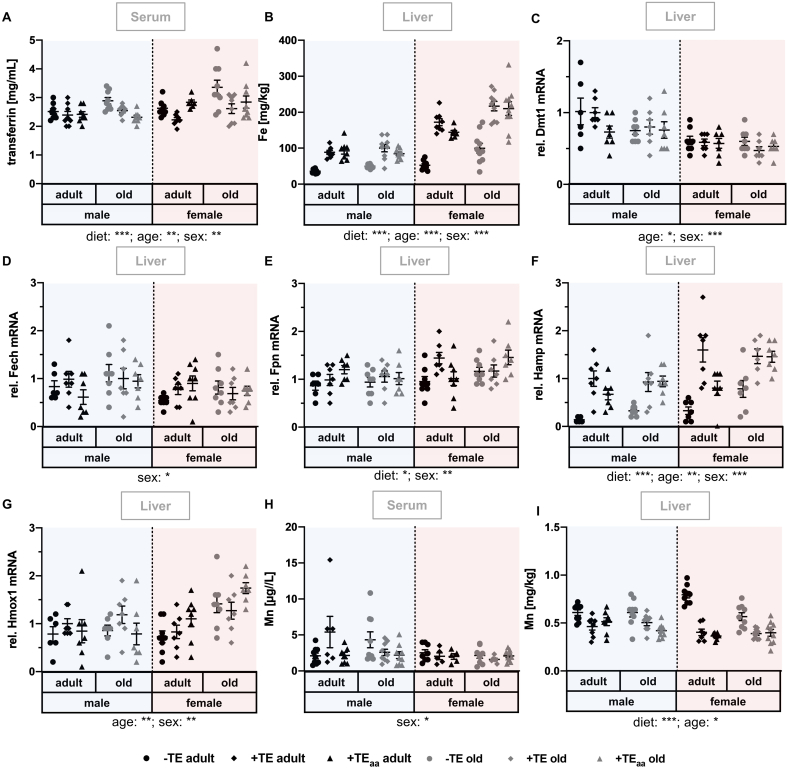
Fig. 4.
Changes in Fe and Mn status, as well as related biomarkers and genes. Markers for the evaluation of the Fe and Mn status were determined in serum and liver of adult (30 weeks) and old (66 weeks) male and female C57BL/6Jrj mice (n = 8–10) receiving a -TE, +TE, or +TEaa diet for 26 weeks. Hepatic Fe (B) as well as serum (H) and hepatic (I) Mn concentrations were determined via ICP-MS/MS. To further evaluate the Fe status, serum transferrin (A) concentrations were analysed via ELISA and relative hepatic expression levels of genes involved in Fe metabolism including Dmt1 (C), Fech (D), Fpn (E), Hamp (F), and Hmox1 (G) were examined by qRT-PCR analysis. Hepatic transcription levels were normalised to a composite factor based on the house keeper genes Hprt and Rpl13a. Variances are expressed as fold changes compared to +TE male adults (mean +TE male adult = 1). Statistical testing based on Three-Way ANOVA and Bonferroni's post-test with *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Detailed results of statistical testing are summarised in Table 2.