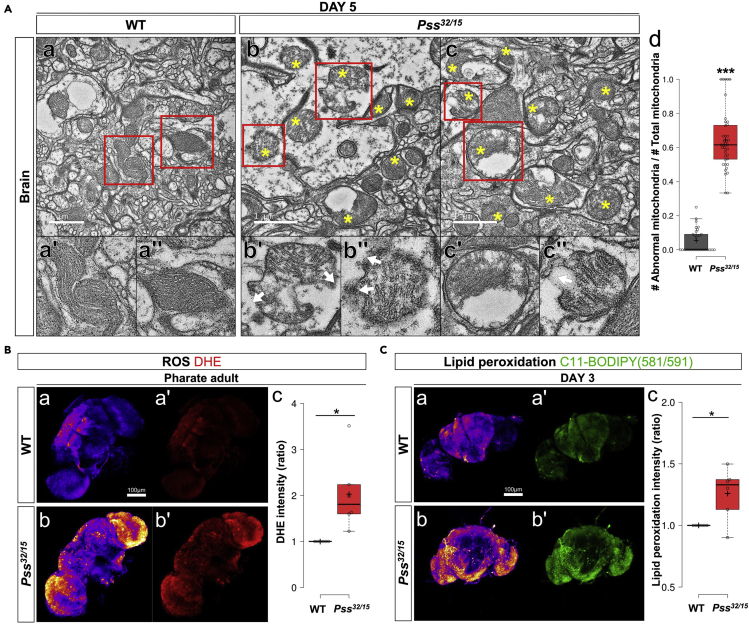
Figure 3.
Pss mutation results in abnormal mitochondrial morphology and increased ROS production in the brain
(A) TEM images of mitochondria in the brain of 5-day-old (a) WT and (b-c) Pss32/15 adults. (a-c) Areas indicated by red boxes in the upper panels are shown at higher magnification in the lower panels (a'-c', a''-c''). (a', a'') WT mitochondria were elliptical with orderly cristae structures. Pss32/15 mitochondria have abnormal shapes (non-elliptical), sizes, and cristae patterns (defective mitochondria are indicated by yellow stars). (b', b'', c'') Occasionally, ruptured mitochondria are observed as indicated by white arrows, and (c') swollen mitochondria are also detected. Scale bar, 1 μm. (e) Quantification of abnormal mitochondria. Data points indicate the ratio of the 'number of abnormal mitochondria/number of total mitochondria' observed from the different TEM figures. ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(B) Detection of ROS in the brain with dihydroethidium (DHE). (a, a') Pharate adult WT. (b, b') Pharate adult Pss32/15. Enhanced ROS production was found in the brain of Pss mutants. (a, b) Images are shown in 'fire' mode for better contrast. (c) Boxplots showing quantification of the DHE intensities. At least five specimens were measured for quantification. Scale bar, 100 μm. ∗p < 0.05.
(C) Detection of lipid peroxidation in the brains by C11-BODIPY(581/591). (a, a') 3-day-old WT. (b, b') 3-day-old Pss32/15. (a, b) Images of the green fluorescent signals were converted to 'fire' modes for better contrast. (c) Boxplots showing quantified fluorescence intensities. At least five specimens were used for the quantification. Scale bar, 100 μm. ∗p < 0.05.