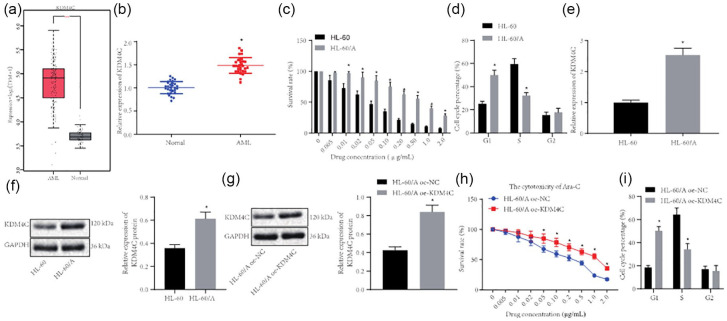
Figure 1.
KDM4C is upregulated in bone marrow tissue samples from AML patients and in the HL-60/A cell line. (a) Analysis of KDM4C expression level in AML based on TCGA (173 bone marrow tissue samples from AML patient) and GTEx (70 normal bone marrow samples) databases. (b) RT-qPCR detection of KDM4C expression in bone marrow tissue samples from 30 AML patients and 30 normal bone marrow samples, *comparison with normal group. (c) MTT assay to analyze HL-60 and HL-60/A viability after Ara-C treatment, *comparison with HL-60. (d) Flow cytometry to study the cell cycle of HL-60 and HL-60/A, *comparison with HL-60. (e) RT-qPCR to detect the expression of KDM4C in HL-60 and HL-60/A, *comparison with HL-60. (f) Western blot to detect the expression of KDM4C protein in HL-60 and HL-60/A cells, *comparison with HL-60. (g) Western blot to analyze the efficiency of KDM4C expression in HL-60/A, *comparison with HL-60/A oe-NC. (h) MTT assay to analyze HL-60/A cell viability after oe-KDM4C treatment, *p < 0.05 compared with oe-NC. (i) Flow cytometry to analyze the cell cycle after overexpression of KDM4C in HL-60/A, *comparison with HL-60/A oe-NC. Experiments were repeated three times. Data from two groups was compared by unpaired t-test.
AML, acute myeloid leukemia; Ara-C, cytarabine; NC, negative control; oe, overexpression; RT-qPCR, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas; GTEx, Genotype-Tissue Expression; MTT, 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide.