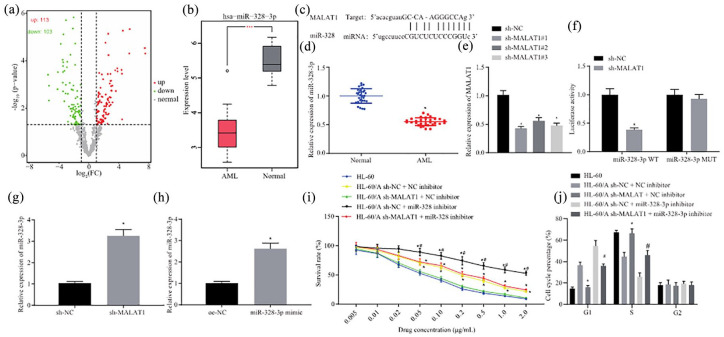
Figure 3.
MALAT1 enhances resistance of AML cells to Ara-C by suppressing miR-328-3p. (a) Volcano analysis of differentially expressed miRNAs in AML by whole blood NGS (GSE128079). (b) miR-328-3p expression in AML based on whole blood NGS (GSE128079). (c) starBase prediction of the binding between MALAT1 and miR-328-3p. (d) RT-qPCR to detect the expression of miR-328-3p in bone marrow tissue samples from AML patients and normal bone marrow samples, *p < 0.05 compared with normal group. (e) RT-qPCR to detect the expression of MALAT1 after transfection with MALAT1 shRNA in HL-60/A, *p < 0.05 compared with normal group. (f) Dual-luciferase reporter assay to analyze the relationship between MALAT1 and miR-328-3p, *p < 0.05 compared with sh-NC. (g) RT-qPCR to detect the expression of miR-328-3p after knockdown of MALAT1 in HL-60/A, *p < 0.05 compared with sh-NC. (h) RT-qPCR to detect the overexpression of miR-328-3p in HL-60 and HL-60/A cells, *p < 0.05 compared with oe-NC. (i) MTT assay to analyze the viability of HL-60/A cells after knockdown of MALAT1 and overexpression of miR-328-3p, *comparison with sh-MALAT1 + NC inhibitor, #comparison with sh-NC + miR-328-3p inhibitor, p < 0.05. (j) Flow cytometry to analyze the cell cycle of HL-60/A after knockdown of MALAT1 and overexpression of miR-328-3p, *comparison with HL-60/sh-MALAT1 + NC inhibitor, #comparison with sh-NC + miR-328-3p inhibitor, p < 0.05. Experiments were repeated three times. Data from two groups were compared by unpaired t-test. Data among multiple groups were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance.
AML, acute myeloid leukemia; Ara-C, cytarabine; Mut, mutant; NC, negative control; NGS, next-generation sequencing; oe, overexpression; RT-qPCR, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; sh, short hairpin; WT, wild type; MTT, 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide; miR-328-3p, microRNA-328-3p.