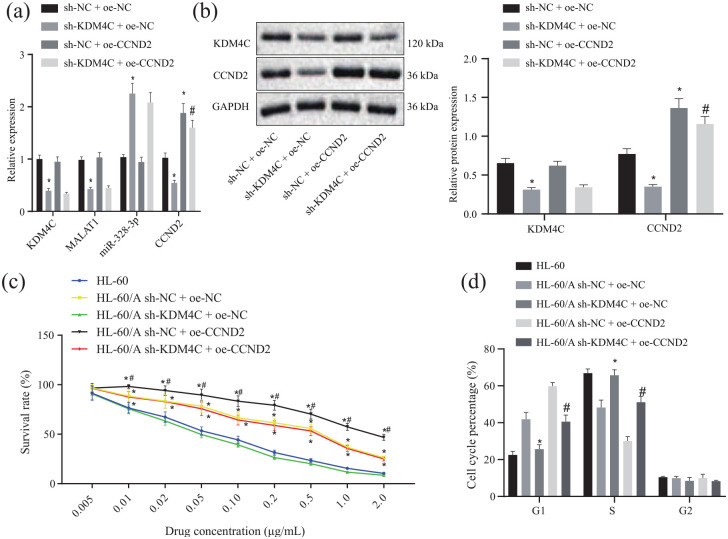
Figure 5.
KDM4C regulates miR-328-3p/CCND2 through MALAT1 leading to Ara-C resistance in AML. (a) RT-qPCR to detect the expression of KDM4C, MALAT1, miR-328-3p, and CCND2 after knockdown of KDM4C or overexpression of CCND2 in HL-60/A cells, *p < 0.05 compared with sh-NC + oe-NC, #p < 0.05 compared with sh-KDM4C + oe-NC. (b) Western blot to detect the expression of KDM4C and CCND2 after knockdown of KDM4C and overexpression of CCND2 in HL-60/A cells, *p < 0.05 compared with sh-NC + oe-NC, #p < 0.05 compared with sh-KDM4C + oe-NC. (c) MTT assay to analyze the viability of HL-60/A cells after knockdown of KDM4C and overexpression of CCND2 in HL-60/A cells, *p < 0.05 compared with HL-60/sh-KDM4C + oe-NC, #p < 0.05 compared with sh-NC + oe-NC/sh-KDM4C + oe-CCND2. (d) Flow cytometry to analyze the cell cycle of HL-60 and HL-60/A cells, *p < 0.05 compared with sh-NC + oe-NC, #p < 0.05 compared with sh-NC + oe-CCND2. Experiments were repeated three times. Data among multiple groups were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance.
AML, acute myeloid leukemia; Ara-C, cytarabine; G1, G1-phase; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; NC, negative control; oe, overexpression; RT-qPCR, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; S, S-phase; sh, short hairpin; MTT, 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide; miR-328-3p, microRNA-328-3p.