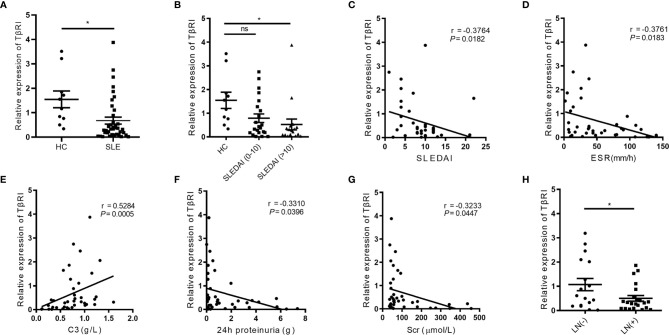
Figure 1.
The TGFβRI expression in naïve CD4+ T cells is lower in SLE patients and correlates with disease-related variables. (A) The level of TGFβRI (TβRI) mRNA in naïve CD4+ T cells was compared among SLE patients (n = 39) and healthy controls (HC) (n = 10). (B) The relative TGFβRI mRNA level of two lupus subgroups was determined, which included moderate to severe disease activity subgroup (SLE disease activity index, SLEDAI>10) (n = 17) and stable and mild disease activity subgroup (SLEDAI 0-10) (n = 22). (C–E) The correlations between TGFβRI mRNA level and SLEDAI, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C3. (F, G) The association between TGFβRI mRNA level and 24-h proteinuria and serum creatinine (Scr). (H) Lower level of TGFβRI mRNA was found in patients with lupus nephritis (LN) (n = 22) than patients without LN (n = 17). Error bars indicate SEM. *P < 0.05. ns, no significant difference.