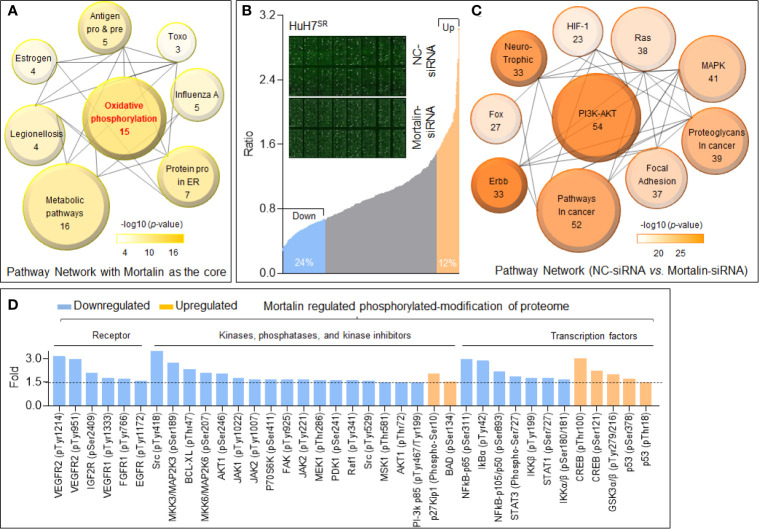
Figure 2.
Mortalin regulates the phosphorylation of cancer-associated proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. (A) Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses of the 20 most frequently altered neighbor interactors and 30 indirect interactors with mortalin from STRING database (Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes). The size of the circle indicates the number of genes enriched in the item, and different color shades indicate the size of p-value. (B) Phospho-antibody microarray analysis of the changes in expression of phosphoproteins following mortalin knockdown in HuH7SR cells. Upregulation of phosphorylation by more than 50% (1.5-fold) is shown in orange, and downregulation of more than 33% (1.5-fold) is shown in blue. (C) KEGG pathway enrichment analyses of the proteins with upregulation or downregulation of phosphorylation of more than 1.5-fold upon mortalin knockdown; the top 10 pathways are shown. (D) Phospho-antibody microarray data showing the phosphorylation levels of critical receptors, kinases, phosphatases, kinase inhibitors, and transcription factors that are involved in the top 5 pathways listed in panel (C) The data presented for each phosphorylation site are the mean of two biological replicates.