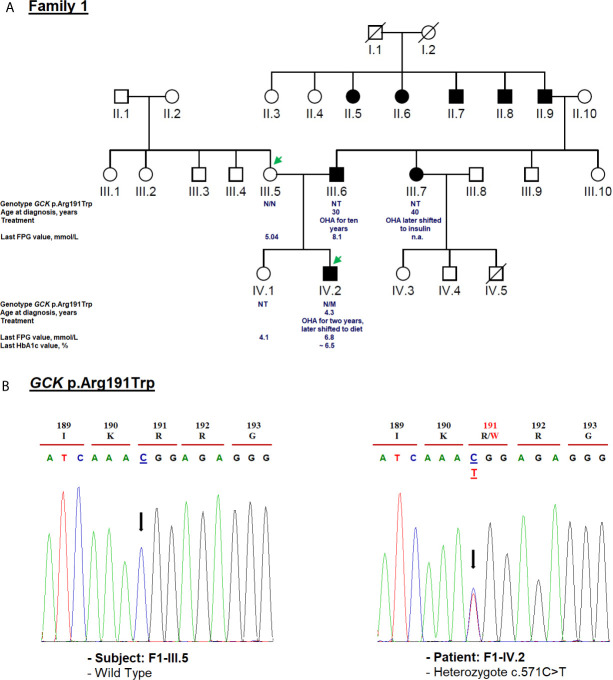
Figure 2.
Mutation analysis of the GCK gene. Panel (A) Pedigree of the family F1 identified with heterozygous GCK variant (NM_000162.5: c.571C>T, p.Arg191Trp). The generations within the family are indicated by roman numerals. Squares and circles represent male and female family members, respectively. Normal individuals are shown as a clear symbol. Black-filled symbols denote patients with diabetes. A line through a symbol denotes the deceased. Green arrows indicate available DNA members. OHA, oral hypoglycemic agents; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; NT, not tested. The genotype is shown underneath each symbol. M and N denote mutant and wild-type alleles, respectively. The age of diabetes onset, glycemic control (the latest FPG or HbA1c measurements), and treatment follow-up are indicated directly below the genotype. Panel (B) Electropherogram analysis of GCK gene in the family F1. Mutated nucleotide on the chromatographs is depicted with an arrow. Amino acid substitution is indicated in red.