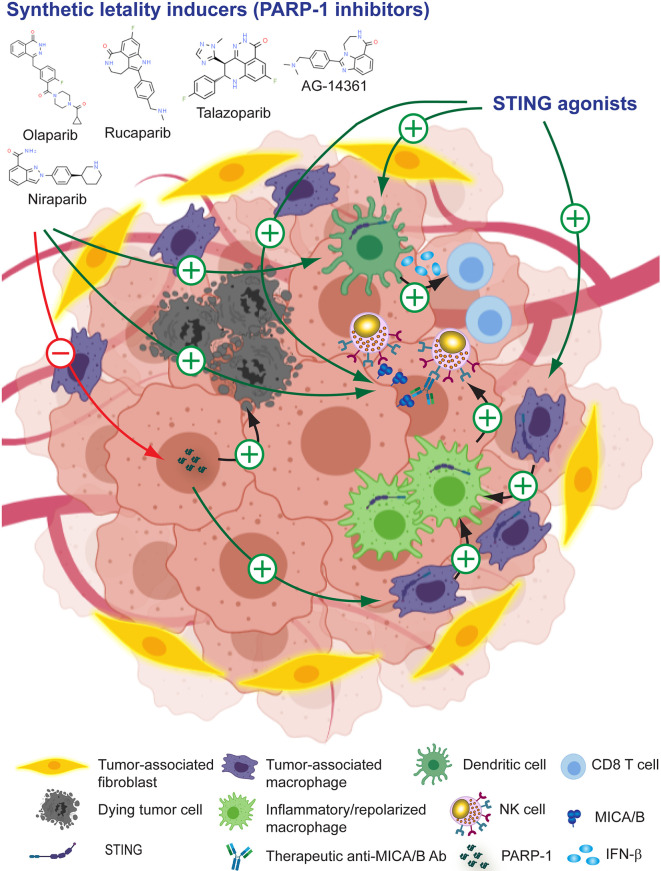
Figure 5.
Leveraging anti-MICA/B Ab therapeutic efficacy through combination therapies with pharmacologic PARP1 inhibitors or STING agonists. The use of PARP1 inhibitors can promote tumor cell death and unleash the activation of STING. Immunogenic cell death and STING activation induce the remodeling of the TME, resulting in a heightened production of IFN-β by DC and CTL-mediated tumor eradication, and a reprogramming of TAM into pro-inflammatory macrophages. These pro-inflammatory macrophages, instead of inhibiting NK cells, might now promote efficient NK cell effector functions. In addition, PARP1 inhibition and STING activation might promote increased expression of MICA/B, resulting in an improved CD16-dependent ADCC of anti-MICA/B Ab, and a recovery of NKG2D-dependent NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor cells. Together, these effects may contribute to foster an efficient tumor cell elimination.