FIGURE 1.
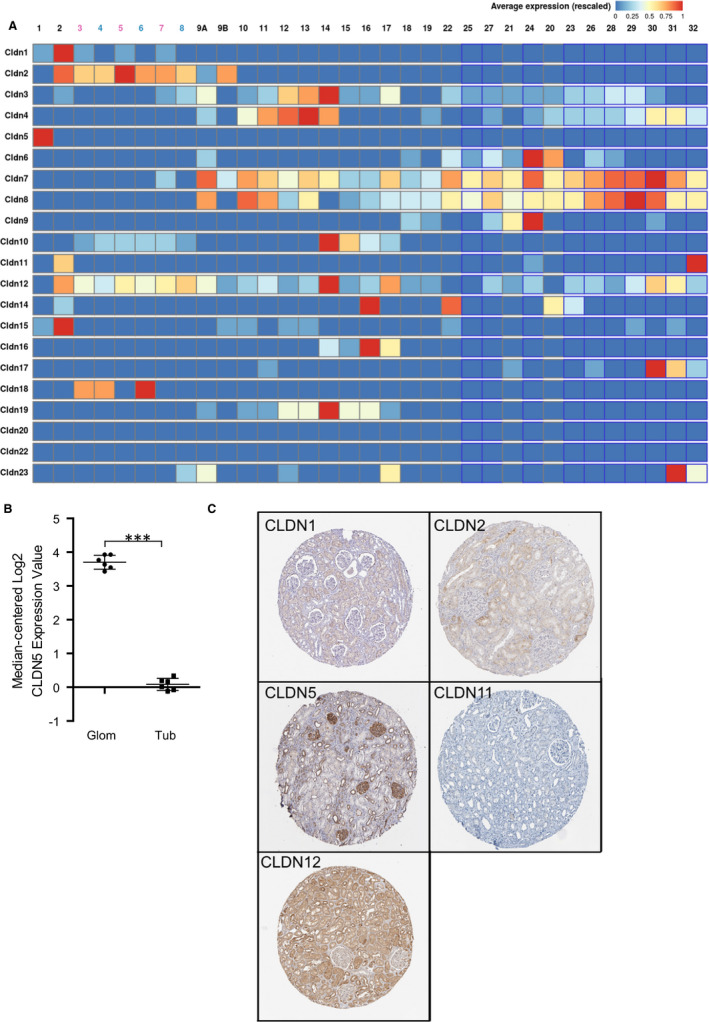
A, Database analysis of CLDN1 to CLDN23 using the Kidney Cell Explorer by Ransick et al14 based on a single‐cell RNA sequencing data set of murine kidneys to determine podocyte‐specific claudins. ID 1 represents podocytes, ID 2 represents parietal epithelial cells and ID 3 following represents tubular cells, as explained in Figure S1 CLDN5 is strongly expressed in ID 1 of the nephron representing podocytes. Other claudins were expressed further distally in the nephron or not expressed at all. B, The results were verified by analysis of the CLDN5 expression based on isolated glomeruli by Lindenmeyer et al,15 which showed a significantly higher median‐centered Log2 CLDN5 expression in the glomerulus compared to the tubule apparatus. ***P < .001 C, Evaluation of immunohistochemistry stainings of CLDN1, 2, 5, 11 and 12 from the Proteinatlas database16 to investigate murine glomerular claudin expression. CLDN1 was expressed in parietal epithelial cells but not in podocytes. CLDN5 was expressed broadly in the glomerulus with accentuated linear staining along the glomerular capillaries indicating localization to podocyte foot processes or the slit diaphragm. CLDN 2 and 12 were expressed mainly in the tubular system. CLDN 11 showed overall low antibody enhancement in kidney sections
