FIGURE 4.
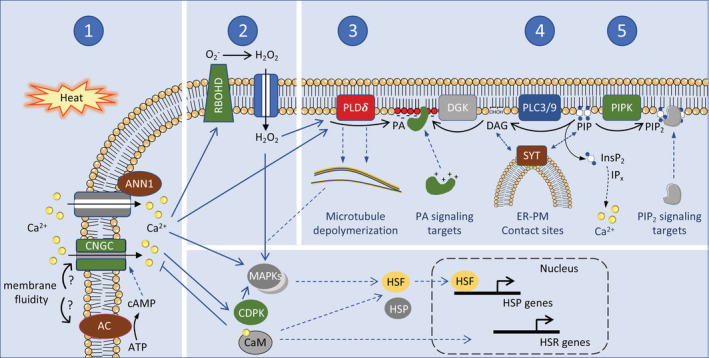
Sensing and primary signalling events of heat stress at the plasma membrane. In response to heat stress (37–45°C, 3–20 min), several plasma membrane‐linked protein activities are triggered which lead to intracellular signals that collectively regulate the heat stress response in plants. 1, Heat perception gives rise to increases in Ca2+, which can enter the cytosol from the apoplast through channels such as CNGC6. This channel might be activated by cAMP, which likely accumulates under heat stress through a membrane‐associated adenylyl cyclase (AC). The latter could be activated as membrane fluidity increases. Through association with calmodulin (CaM), Ca2+ can negatively regulate CNGC6, and promote the function of HSFs. HSFs are the primary regulators of the heat response leading to transcriptional induction of HSPs and other genes. Apart from CNGC6, Annexin 1 (ANN1) may function to increase cytosolic Ca2+. 2, The second major factor in the heat stress response is H2O2, which is generated by the plasma membrane microdomain NADPH oxidase, RBOHD, whose activity is modulated by several factors, including Ca2+ and PA. After H2O2 enters the cell, it modifies the PLDδ protein such that it becomes sensitive to activation by Ca2+. 3, PLDδ generates PA, which has a myriad of signalling functions that are mediated by its interaction with cytosolic target proteins. PLDδ is attached to microtubules and its activity leads to microtubule depolymerization. Moreover, H2O2 can activate HSFs through MAPK signalling. 4, PLC3 and PLC9 are required for sHSP induction and thermotolerance. Most likely, they hydrolyze PIP to generate DAG, releasing the inositol‐bisphosphate (IP2) headgroup. DAG can be phosphorylated to PA by diacylglycerol kinase (DGK). In plants, rather than IP2 or IP3, inositol's more highly phosphorylated derivatives are the likely inducers of cytosolic release of Ca2+. DAG could associate with synaptotagmin (SYT) in the ER at ER‐PM contact sites, which may function to stabilize the plasma membrane under stress, and facilitate the exchange of lipids between the plasma membrane and the cortical ER. 5, Besides PA, also PIP2 accumulates under heat stress, through PIP kinase (PIPK) activity, first only in the plasma membrane, later also in internal structures, including the nucleolus and cytosolic foci. PIP2 regulates effector proteins through specific lipid‐binding domains
