FIGURE 6.
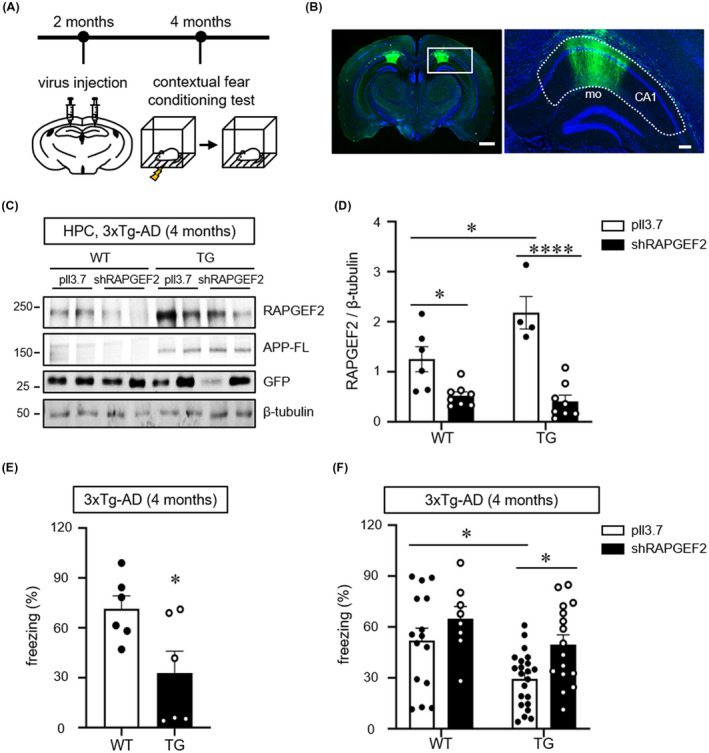
Knockdown of RAPGEF2 rescues fear memory deficits in 4‐month‐old 3xTg‐AD mice. A, Time course of stereotaxic delivery of lentiviral particles and behavioural tests. B, Representative image of GFP expression in the hippocampal CA1 area. Lentiviral particles simultaneously expressing shRAPGEF2 and GFP were bilaterally injected into the hippocampal CA1 area. Hoechst dye was used to stain neuronal nuclei (blue). Scale, 10 μm. Right, higher magnification image enclosed in rectangles at the left. A dotted line indicates the CA1 (mo: molecular layer in dentate gyrus). 53% ± 0.9% area of CA1 region was GFP‐positive (virus transduced) (n = 3). Scale, 200 μm. C, Virus‐mediated knockdown extent of RAPGEF2 in vivo. Lentiviral particles expressing either shRAPGEF2 or a control empty vector (pll3.7) were transduced into hippocampal CA1 area in 2 months of wild‐type (WT) and 3xTg‐AD (TG) mice. After 2 months, hippocampal lysates were used for western blot analysis for RAPGEF2. APP‐FL (full length APP) were used as the marker of TG mice. D, Quantification of RAPGEF2 levels normalised to β‐Tubulin. pll3.7 in WT, n = 6 (5 males, 1 female); shRAPGEF2 in WT, n = 8 (7 males, 1 female); pll3.7 in TG, n = 4 (3 males, 1 female); shRAPGEF2 in TG, n = 8 (7 males, 1 female). E, The contextual fear memory test in 4‐month‐old wild‐type (WT) and 3xTg‐AD (TG) mice (n = 6, males). F, Control (pll3.7) or shRAPGEF2‐expressing viral particles were injected into the hippocampal CA1 area in 2‐month‐old WT and 3xTg‐AD mice. After 2 months, the contextual fear memory test was performed (pll3.7 in WT, n = 15 males; shRAPGEF2 in WT, N = 8 males; pll3.7 in 3xTg‐AD mice, n = 22 males; shRAPGEF2 in 3xTg‐AD, n = 17 males). All data are shown as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001; two‐tailed unpaired Student's t‐test (E) and Two‐way ANOVA, Tukey's multiple‐comparison test (D and F)
