FIGURE 1.
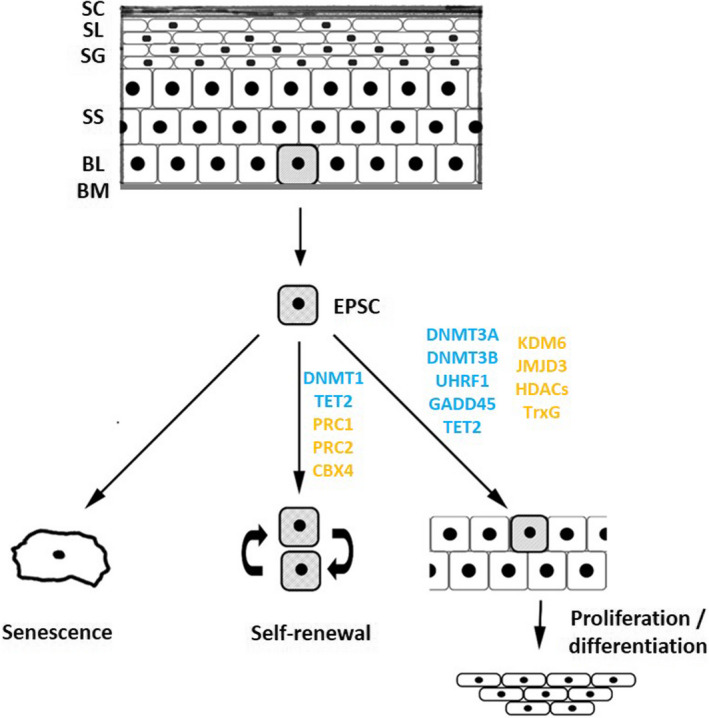
Epigenetic effectors and epidermal homeostasis. Maintenance and differentiation of EPSCs critically governs epidermal homeostasis. Individual, proliferating EPSCs (indicated as shaded cells) are located in the basal layer. As cells differentiate, they progressively move upward through the various layers of the epidermis. Eventually, these cells lose their nuclei before forming the layers of the outermost stratum corneum. Multiple epigenetic effectors regulate EPSC self‐renewal, proliferation and differentiation. These factors control DNA methylation (indicated in blue), histone modification and chromatin remodelling (indicated in orange). Abbreviations: BL, basal layer; BM, basement membrane; DNMT, DNA methyltransferase; EPSC, epidermal stem cell; HDAC, histone deacetylases; PRC, polycomb repressive complex; SC, stratum corneum; SG, stratum granulosum; SL, stratum lucidum; SS, stratum spinosum; TET, ten‐eleven translocation; TrxG, trithorax group proteins
