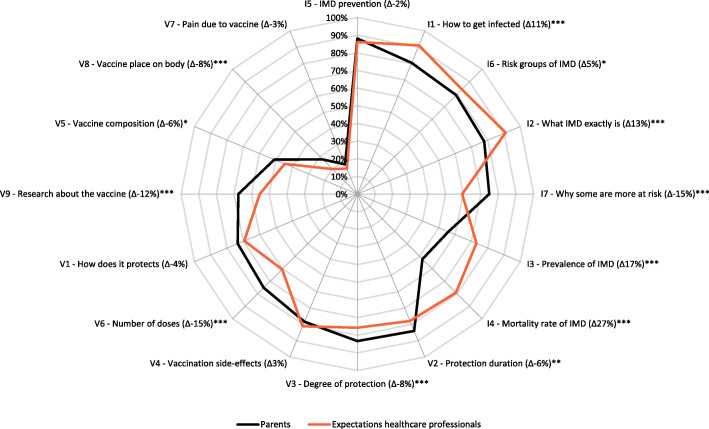
Fig. 2.
Percentages of parents who perceived information items about IMD (I1–7)# and the menACWY vaccination (V1–9)# as important, and percentages of healthcare professionals who expected that parents would perceive these information items as important. The information items are ranked clockwise (most important to least important as indicated by parents), separately for I items and V items. # The numbers of the information items in the Figure correspond to the information items in Table 1. ∆ Difference between the percentage of parents that indicated an item as important to them and the percentage of healthcare professionals that expected that parents would indicate this item as important to them. A positive difference indicates higher expected importance in healthcare professionals than indicated by parents, and a negative difference indicates a lower expected importance by healthcare professionals than indicated by parents. * Significant (p < 0.05) difference between the percentage of parents indicating an item as important/less important to them and the percentage of healthcare professionals expecting that parents would indicate this item as important/less important. ** Significant (p < 0.01) difference between the percentage of parents indicating an item as important/less important to them and the percentage of healthcare professionals expecting that parents would indicate this item as important/less important. *** Significant (p < 0.001) difference between the percentage of parents indicating an item as important/less important to them and the percentage of healthcare professionals expecting that parents would indicate this item as important/less important