Fig. 3.
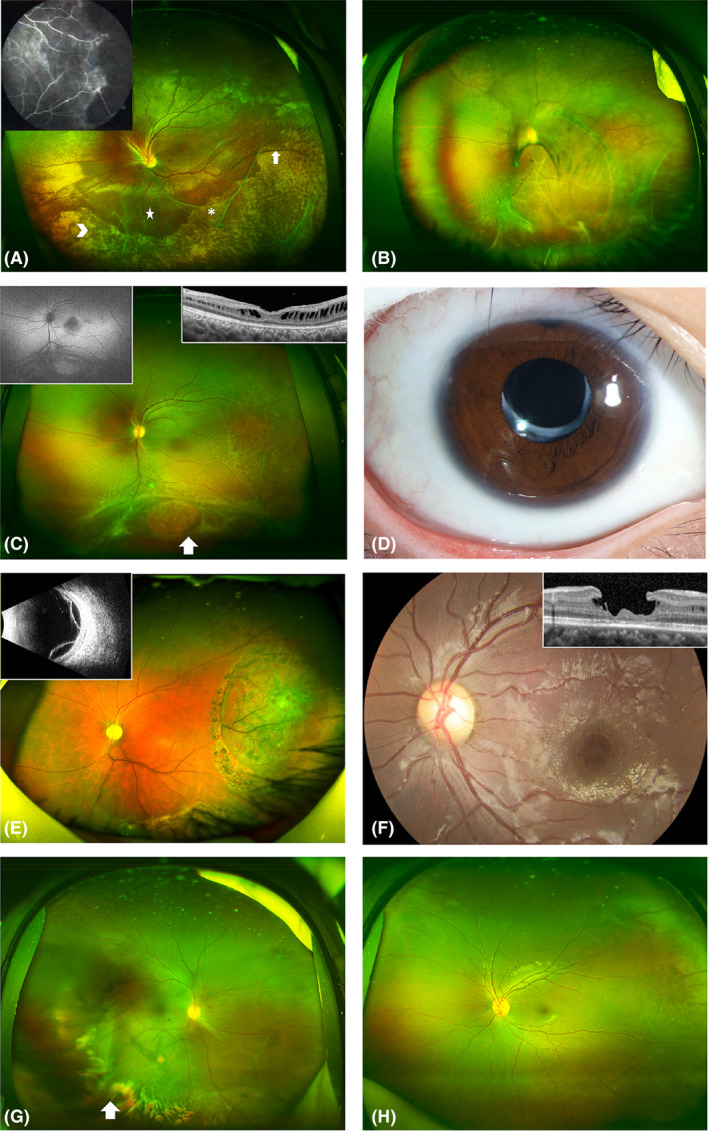
Representative ultra‐wide‐field fundus appearance depicting complications in patients with X‐linked retinoschisis. (A) Patient with peripheral schisis and multiple vitreous veils (asterisk) connected to the retina with bridging vessels (white arrows). A large amount of yellow‐white exudation (arrowhead) is seen at the inferior temporal area. The five‐pointed star at the inferior area indicates vascular sheathing. Peripheral retinal schisis at the superior area causes distortion of the optic disc. The image in the upper left corner is the corresponding fluorescein angiogram, which shows large areas of nonperfusion at the peripheral retina. (B) Patient with retinal detachment at the inferior temporal area, and multiple vitreous veils connected to the retina with bridging and tortuous vessels. A pigmented demarcation line is seen at the posterior pole. An occluded blood vessel appears as a white line at the inferior area. (C) Patient with typical white spots in the posterior pole, and multiple vitreous veils connected to the retina with bridging vessels. White arrow indicates a large inner retinal break. The image in the upper left corner is the corresponding autofluorescence, which shows hypoautofluorescence at the fovea area. The image in the upper right corner shows corresponding OCT changes. OCT shows lamellar schisis and mild macular atrophy. (D) Patient with cataract after intraocular lens implantation. (E) Patient with bullous retinal detachment after retinal photocoagulation. The image in the upper left corner is the corresponding ultrasound B image. (F) Representative ultra‐wide‐field fundus of a patient with an inner macular hole. The image in the upper right corner shows corresponding OCT changes. OCT shows an inner macular hole with an intact outer structure of the retina. (G) Patient with mild vitreous haemorrhage. (H) Patient with a typical cartwheel‐like appearance in the central macula and peripheral retinal splitting at the inferior area.
