FIGURE 5.
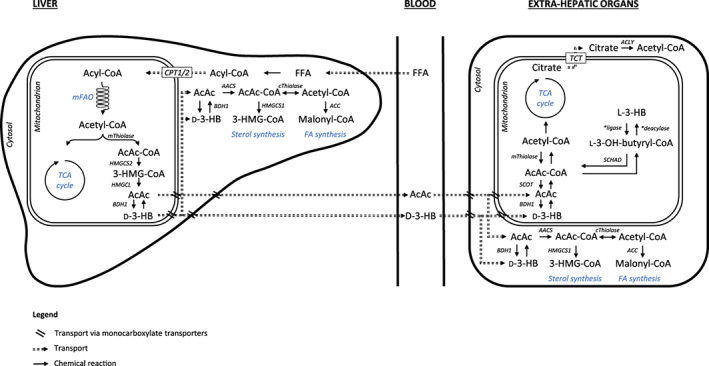
Schematic representation of the proposed production and utilization of ketone bodies. D‐3‐HB is primarily formed in the liver via the 3‐hydroxy‐3‐methylglutaryl‐CoA pathway, whereas the route of endogenous L‐3‐HB synthesis remains to be fully elucidated. In mitochondria, acetoacetyl‐CoA can be converted to L‐3‐HB‐CoA, and subsequently formed to L‐3‐HB via a specific CoA deacylase,45 however this conversion does not appear to take place in the liver.46 D‐3‐HB is oxidized to AcAc in extrahepatic tissues and subsequently reconverted to two molecules of acetyl‐CoA which enter the Krebs cycle.35 In contrast, a specific CoA ligase activates L‐3‐HB to L‐3‐hydroxybutyryl‐CoA after mitochondrial import.29 L‐3‐hydroxybutyryl‐CoA is metabolized to acetyl CoA by short‐chain acyl‐CoA dehydrogenase.33, 45, 47 Next to energy generation, non‐oxidative fates of KB may include fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis. Abbreviations (in alphabetical order): 3‐HMG‐CoA, 3‐hydroxy‐3‐methylglutaryl‐CoA; AcAc, acetoacetate; AcAc‐Coa, acetoacetyl‐CoA; AACS, acetoacetyl‐CoA synthetase; ACC, acetyl‐CoA carboxylase; ACLY, adenosine triphosphate citrate lyase; BDH1, D‐3‐hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase; CoA, coenzyme A; CPT1, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1; CPT2, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2; cThiolase, cytosolic thiolase; D‐3‐HB, D‐3‐hydroxybutyrate; FA, fatty acids; FFA, free fatty acids; HMGCL, 3‐hydroxy‐3‐methylglutaryl‐CoA lyase; HMGCS1, 3‐hydroxy‐3‐methylglutaryl‐CoA synthase 1; HMGCS2, 3‐hydroxy‐3‐methylglutaryl‐CoA synthase 2; L‐3‐HB, L‐3‐hydroxybutyrate; L‐3‐OH‐butyryl‐CoA, L‐3‐hydroxybutyryl‐CoA; mFAO, mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation; mThiolase, mitochondrial thiolase; SCHAD, short‐chain 3‐hydroxyacyl‐CoA dehydrogenase; SCOT, succinyl‐CoA‐3‐oxoacid‐CoA transferase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; TCT, tricarboxylate transport
