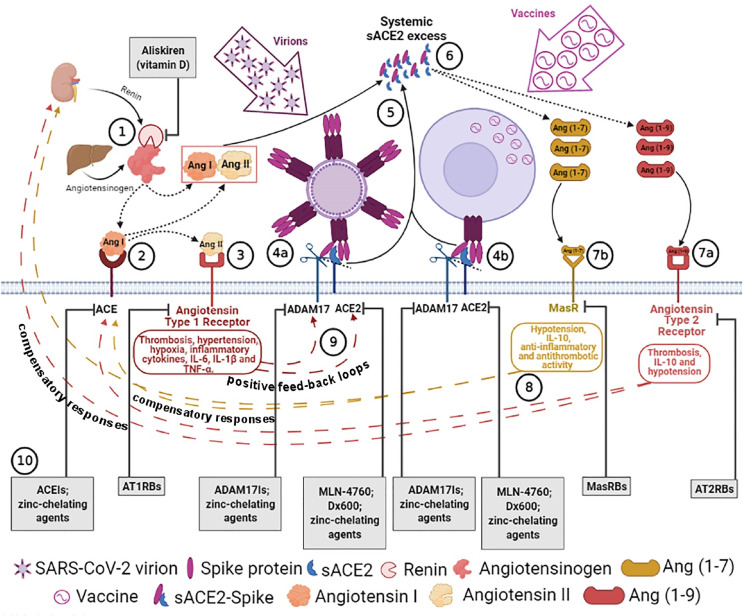
Fig. 1.
Putative physiopatological mechanisms leading to COVID-19 after SARS-CoV-2 infection or possibly to mild adverse reactions following vaccination and treatment proposals. 1) Renin secreted, by the kidney, cleaves angiotensinogen, produced by liver, to form Ang I, 2) Ang I is converted to Ang II by pulmonary ACE zinc-metalloprotease. 3) Ang II binds to angiotensin type 1 receptors (AT1Rs) or it is transformed into Ang (1–7) by ACE2 zinc-metalloprotease (see 6). 4a) SARS-CoV-2 spikes of virions or 4b) of “vaccinated” cells bind to ACE2, inducing ADAM17-mediated ACE2 shedding, which is possibly driven by spike N-terminal domain binding/recruitment of ADAM17 close to ACE2. 5) ADAM17-regulated ectodomain shedding of ACE2 results in increased amount of soluble and active circulating ACE2 (sACE2). 6) sACE2 can transform both Ang I and Ang II into Ang (1–9) and Ang (1–7), respectively. 7) The excess of Ang 1–9 and Ang 1–7 signalling via the AT2Rs (7a) and MasRs (7b) can induce hypotension, anti-inflammatory (IL-10), antithrombotic or prothrombotic pathway activation. 8) Differently from vaccination, in susceptible subjects (expressing high baseline levels of sACE2 activity), the persistent activation of these pathways caused by viral expansion will, in turn, produce late compensatory responses that upregulate both renin and ACE expression, leading to an excess of Ang II. 9) The excess of Ang II through AT1R hyperactivation can cause thrombosis, hypertension, hypoxia, inflammation, IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α, which establish positive feedback loops by inducing further ACE2 and ADAM17 upregulation (for further details, see the text). 10). In the grey bottom boxes, drugs inhibiting RAS enzymes that can potentially stop compensatory responses and/or positive feedback loops (depending on COVID-19 phase) are indicated (for further details, see the text). Receptor Blockers: AT1RBs, AT2RBs, MasRBs and enzymatic inhibitors: ACEIs, ACE2Is, ADAM17Is, are indicated. Dotted arrows indicate an enzymatic transformation, dashed arrows represent compensatory responses and positive feedback loops, and full arrows indicate releases in systemic circulation. Created in Biorender.com.