FIGURE 3.
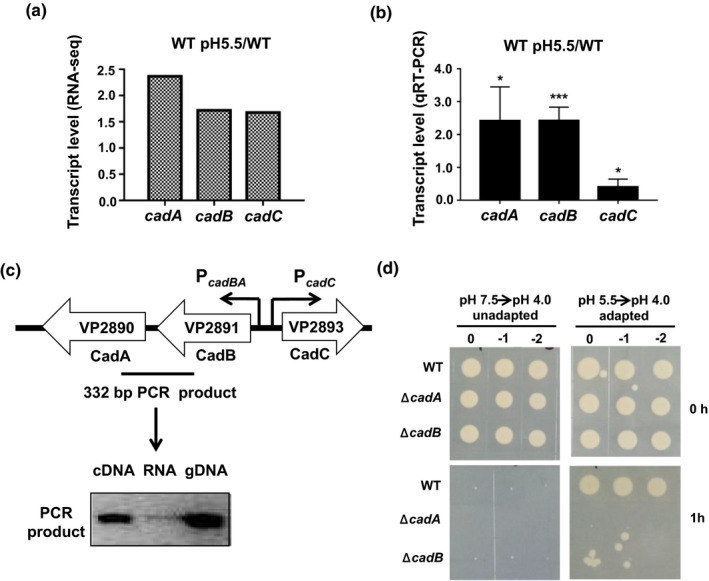
CadBA is responsible for the ATR in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. (a) The cadBA and cadC mRNA levels based on the RNA‐seq. (b) qRT‐PCR analysis of the cadBA and cadC mRNA levels under the sub‐lethal acidic condition. The results are shown normalized to the gyrB mRNA levels and were determined by the ΔΔCT method. The differences are shown relative to the levels at pH 7.5. *p < .05, ***p < .001, t test. (c) The genetic environment of the cadBA‐cadC genes in V. parahaemolyticus chromosome. Arrows indicate the predicted promoter regions and RT‐PCR was used to determine whether cadA and cadB are co‐transcribed. (d) The survival of V. parahaemolyticus. The WT, ΔcadA, and ΔcadB strains were exposed to the lethal acidic pH (4.0, HCl) for 1 hr with or without preadaptation at the sub‐lethal acidic pH (5.5, HCl) for 1 hr. The bacteria were then serially diluted (10‐fold) and spotted onto LB agar plates [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
