Fig 5.
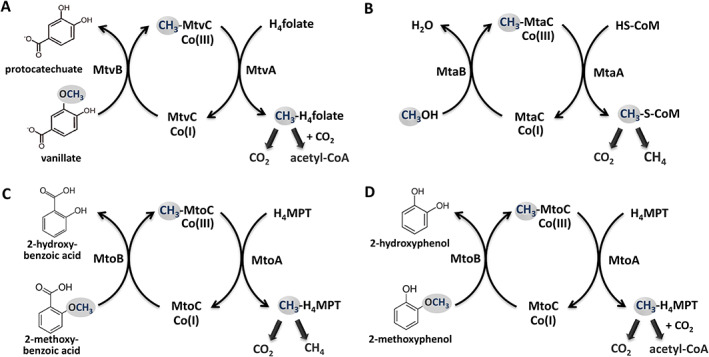
Demethylation and demethoxylation pathways of methoxydotrophic archaea in comparison to methylotrophic methanogens and acetogenic bacteria. (A) Demethoxylation pathway as described for the acetogenic bacterium Moorella thermoacetica, modified from Pierce et al. (Pierce et al., 2008). (B) Demethylation pathway in methanogenic archaea when using methanol as substrate. (C) Demethoxylation pathway of the methanogen M. shengliensis (Mayumi et al., 2016; Kurth et al., submitted). (D) Tentative demethoxylation pathway of A. fulgidus. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis revealed cobalamin binding protein MtoC (AF_0006) and its activator MtoD (AF_0010), O‐demethylase MtoB (AF_0007) and methyl transferase MtoA (AF_0009) to be essential for growth of A. fulgidus on methoxylated aromatic compounds. CoM: coenzyme M, H4folate: tetrahydrofolate, CO(III): cobalamin binding protein, H4MPT: tetrahydromethanopterin. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
