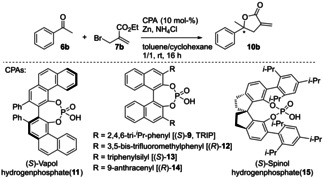
Table 2.
Screening of different chiral phosphoric acid (CPA) catalysts.
|
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Entry |
Chiral Phosphoric Acid (CPA) |
Conv. [%][a] |
ee [%][b] |
|
1 |
(S)‐11 |
>99 |
<1 |
|
2 |
(R)‐12 |
>99 |
17[c] |
|
3 |
(S)‐13 |
>99 |
27 |
|
4 |
(S)‐15 |
>99 |
33[d] |
|
5 |
(R)‐14 |
>99 |
44[c] |
|
6 |
(S)‐9 |
>99 |
70 |
Reaction conditions: ketone (0.1 mmol), zinc (5 eq.), NH4Cl (8 eq.), CPA (10 mol‐%), 7 b (1.5 eq.) in toluene (1 mL) and cyclohexane (1 mL); spontaneous lactonization to product 10 b was observed for all entries.
[a] Conversions were determined via HPLC‐UV (215 nm).
[b] The enantiomeric excess was determined on a chiral stationary phase via normal phase HPLC‐UV (215 nm).
[c] The opposite enantiomer was observed [note: the (R)‐CPA has been used in case of these entries].
[d] The opposite enantiomer was observed [note: reagent 7d was used in case of this entry].