FIGURE 3.
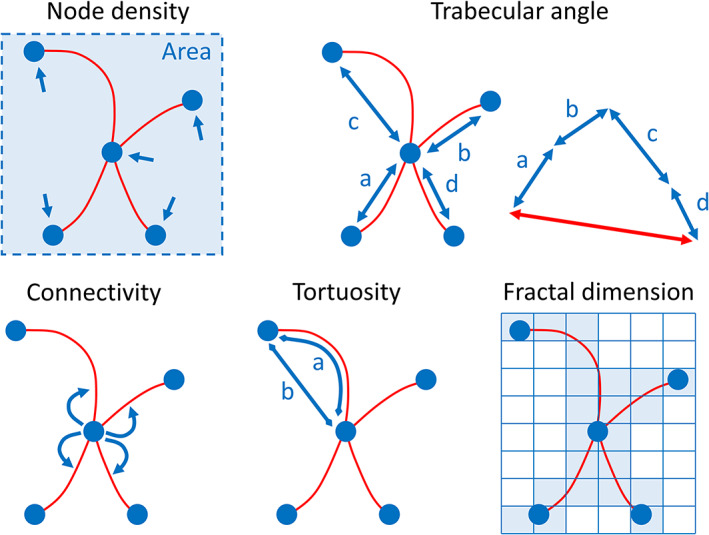
Graphical intuition of the indices measured on the topological skeleton of cancellous bone. For ease of visualization, the indices are shown for a 2D topological skeleton. Node density is represented by the number of nodes per unit area and it is calculated using a kernel density approximation over a discretized space. The trabecular angle (degrees) is measured between a reference axis (not shown) and the unitary resultant (red, double‐headed arrow) of all trabecular directions (blue, double‐headed arrows) obtained by vector sum. Connectivity is the mean number of branches connected to non‐terminal nodes. Tortuosity is the ratio between the arc length of a branch and the linear distance between its starting and ending nodes (a/b). Fractal dimension is an index of complexity measured on the coordinates of the skeleton using the box‐counting algorithm. In this approach, discrete regular grids of decreasing cell size are superimposed over the cancellous skeleton and the number of cells occupied by the skeleton are counted for each grid. Fractal dimension is the slope of the line fitting the number of cells that overlap the skeleton versus the inverse of the cell size
