FIGURE 2.
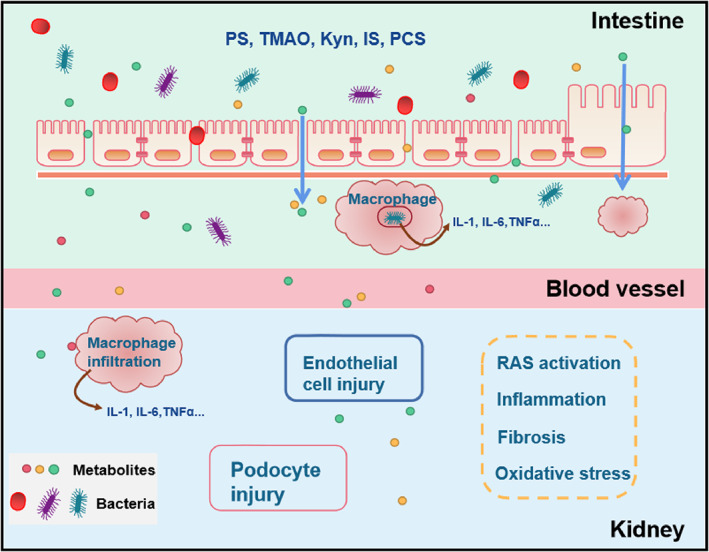
The mechanism of gut microbiota on the kidney. The gut microbiota itself and its metabolites can enter the Interstitial fluid through the increased permeability of the intestinal mucosa. Macrophages can phagocytose bacteria and release inflammatory factors. Metabolites and inflammatory factors enter the blood, reach the kidneys and cause damage to endothelial cells and podocytes through the activation of the RAS system, inflammation and oxidative stress. phenyl sulphate (PS); Trimethylamine‐N‐oxide (TMAO); Kynurenine (Kyn); Indoxyl Sulphate (IS); p‐cresol sulphate (PCS); Interlrukin 1 (IL‐1); Interlrukin 6 (IL‐6); Tumour Necrosis Factor (TNFα); Renin‐angiotensin System (RAS)
