Figure 1.
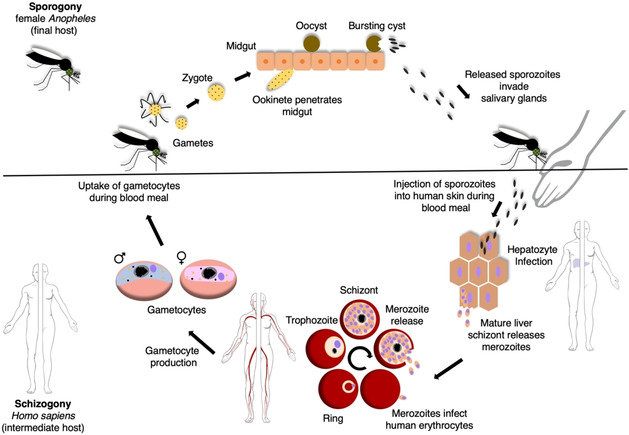
Life cycle of human‐pathogenic Plasmodium parasites. The asexual reproduction (schizogony, lower panel) takes place in the human intermediate host, while the sexual replication (sporogony, upper panel) occurs in the final host. During their life cycle, Plasmodium parasites are able to infect several cell types of the human host such as hepatocytes (liver schizogony) and RBCs (erythrocytic schizogony). Sexual precursor cells, so‐called gametocytes, are ingested by a female Anopheles mosquito during the blood meal and mate within the midgut after their maturation into gametes. The newly formed zygote further matures into an ookinete, which migrates across the midgut epithelial cells. After settling beneath the epithelial cells, the ookinete rounds up to form a sporozoite‐producing oocyst. The produced sporozoites are then inoculated into the human host during the mosquitoes’ next blood meal. Modified with permission from ref. [167]. Copyright: 2020, Wiley. Image credit for pictograms: Human Protein Atlas.[168]
