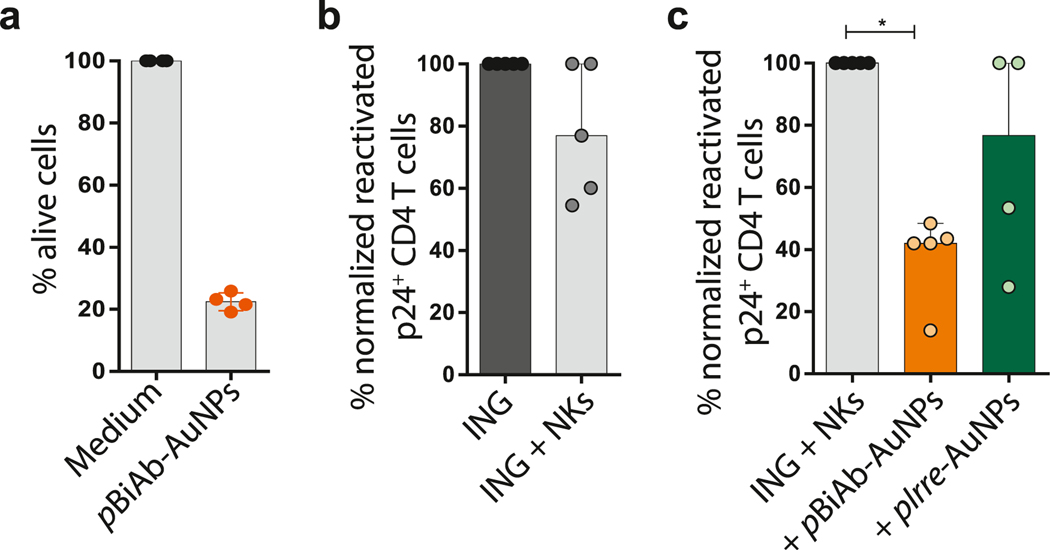
Fig. 5.
The pBiAb-AuNPs enhance the killing of the latently HIV-infected cells after viral reactivation. (a) Cytotoxic response against latently-infected ACH-2 cells after viral reactivation. PHA and PMA-reactivated ACH-2 cells were cultured with primary NK cells at ratio 1:10 target/effector for 4 h in the presence or absence of the pBiAb-AuNPs at 10 μg/ml. Cytotoxicity was calculated as the disappearance of ACH-2 target cells using flow cytometry count beads. Data is normalized to the control condition in absence of the pBiAb-AuNPs. Mean with SD of 4 independent experiments is shown. (b) Graph representing the cytotoxic response mediated by NK cells in a primary cell model of HIV latency and after viral reactivation with Ingenol (ING) (100 nM) (ratio reactivated cells:NK cells 1:1) in the absence of pBiAb-AuNPs. Median with range of n = 5 experiments is represented. (c) Summary graph of the enhancement of the NK-mediated cytotoxic response against viral reactivated CD4+ T cells induced by the presence of the pBiAb-AuNPs or Irre-AuNPs (2.5 μg/ml total antibody burden) (n = 5). Median with range is represented. Statistical comparisons were performed using the one sample t-test. *p < 0.05.