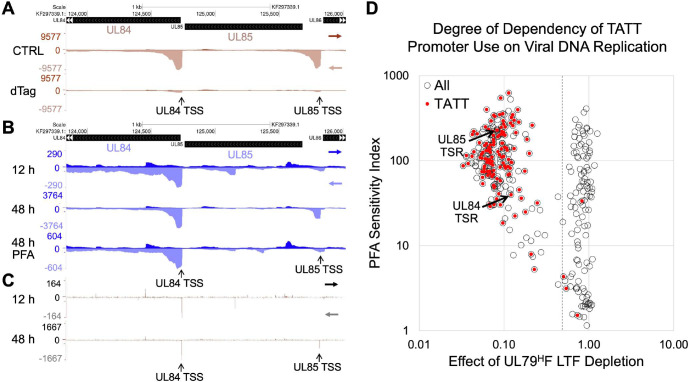
Fig 6. The UL79 LTF initiates transcription at TATT-containing viral early-late and late promoters.
(A-C) Genome browser views of PRO-Seq-Flavo results for TATTTAA-containing UL84 and UL85 promoters. Spike-in normalized reads from Pol II nascent transcripts are aligned to the HCMV TB40/E KF297339 genome. (A) HCMV TB40/E UL79HF infection for 72 h treated with 6-h dTag vs. CTRL. (B and C) HCMV TB40/E WT infections for 12 and 48 h (in absence or presence of PFA). Panel C is a map of 5’-ends of the same reads aligned in panel B for 12-h and 48-h infections without PFA. Vertical arrows point to positions of UL84 and UL85 MAXTSS. (D) Scatterplot of PFA sensitivity index (PSI) vs. effect of UL79HF LTF depletion on TSR strength (dTag vs. CTRL treatments) for 320 viral TSRs ≥435 nascent RNA reads (open circles). Viral TSRs having a TATT positioned -40 to -28 upstream of the MAXTSS are marked in red. PSI = ratio of TSR reads for PFA treatment/CTRL treatment of 72-h HCMV TB40/E WT infection. Effect of UL79HF LTF depletion (dTag/CTRL reads) is described in Fig 3B. Dashed line denotes 0.5 dTag/CTRL read breakpoint. Arrows point to UL84 and UL85 TSRs, with PSIs 40 and 220, respectively.