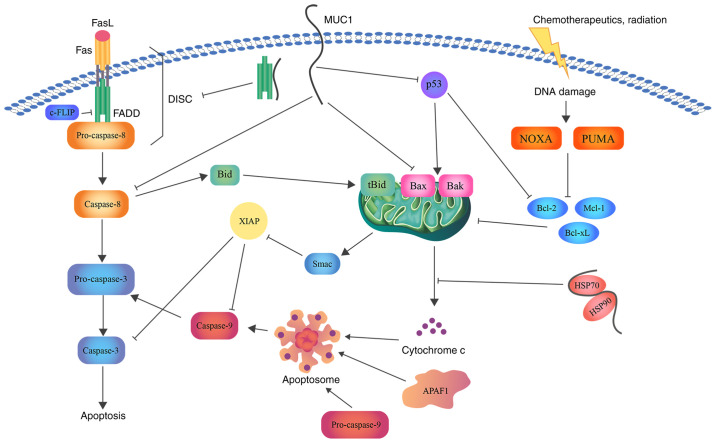
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the role of MUC1 in apoptosis. MUC1 interacts with FADD DED, blocking the formation of DISC and suppressing the induction of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway. Direct association with caspase-8 inhibits its activation. In addition, MUC1-C suppresses Bax translocation to the MOM and cytochrome c release. Binding of MUC1 to the HSP90/HSP70 complex weakens the activation of the mitochondrial pathway. Moreover, direct binding of MUC1 to the p53 regulatory domain is associated with stimulation of growth-arresting gene transcription, thereby inhibiting apoptosis. Bcl, B-cell lymphoma; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; Bcl-xL, Bcl-extra large; MUC1, mucin 1; FADD, FAS-associated with death domain; DED, death effector domain; DISC, death inducing signaling complex; MUC1-C, MUC1 C-terminal subunit; MOM, mitochondrial outer membrane; HSP, heat shock protein; FasL, fatty acid synthetase ligand; FLIP, FLICE (FADD-like IL-1β-converting enzyme)-inhibitory protein; Bid, BH3 interacting domain death agonist; Mcl-1, induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein; NOXA, NADPH oxidase activator; PUMA, p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis; Smac, second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase; XIAP, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein.