FIGURE 3.
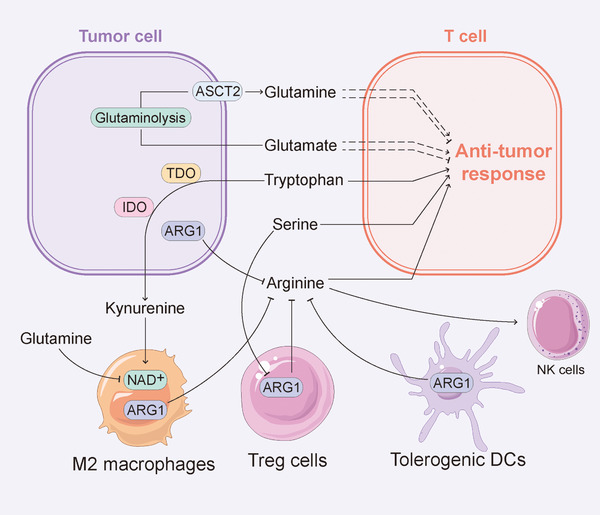
Effect of amino acid metabolism on infiltrating lymphocyte function. Amino acid metabolism plays a critical role in the regulation of immune response. Glutamine and glutamate metabolisms have different effects on the antitumor response of T cells under different states and of different subtypes. The removal of glutamine causes T cell proliferation arrest, while CD8+ T cells cultured under glutamine restriction conditions are more effective in eliminating tumor cells. Arginine is necessary for the activation of Teff cells. Thus, immune regulatory cells and tumor cells can degrade arginine by expressing ARG1 to limit the availability of arginine to T cells, thereby inhibiting antitumor immune activity. Tryptophan deprivation impairs the cell cycle and differentiation of T cells, and TDO and IDO, the catabolic enzymes of tryptophan, are expressed in tumor cells and various stromal cells in the TME to promote tumor progression. Serine is crucial for Teff cell response and reduces the immunomodulatory capacity of Treg cells. Abbreviations: ARG1: arginase 1; ASCT2: alanine‐serine‐cysteine transporter 2; DC: dendritic cell; IDO: indoleamine 2,3‐dioxygenase; NAD: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; Teff: effector T; Treg: regulatory T; TDO: tryptophan 2,3‐dioxygenase; TME: tumor microenvironment
