Figure 7.
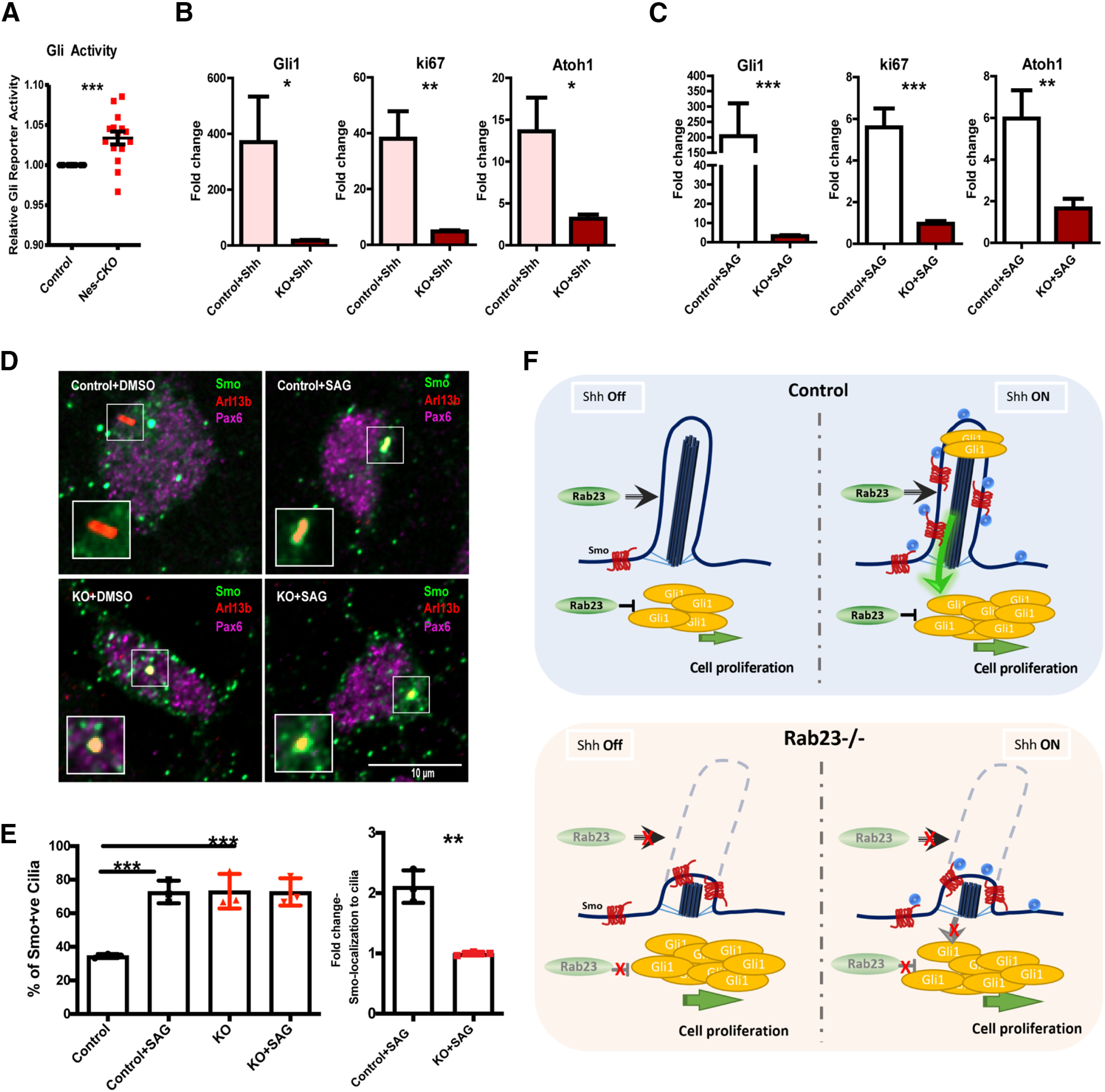
Rab23 regulates basal level and primary cilium-dependent Hh signaling activity. A, Graph depicts relative basal level 7Gli:GFP reporter signals on DIV3 (Day In Vitro) primary GCP cultures. Quantifications show quadruplicates of four independent experiments. Statistical significance, unpaired Student's t test; ***p ≤ 0.0001 B, C, Graphs showing gene expression levels of P7 GCPs primary cultures treated with Shh (B) and SAG (C) on DIV1, respectively. Total RNAs were extracted from DIV2 culture, 24 h after the respective treatments. Quantifications depict double δ Ct values of three independent experiments. δ Ct values of the treated groups were normalized to its respective untreated group, which gave double δ Ct values as plotted. Statistical significance, unpaired Student's t test; ***p ≤ 0.0001, **p ≤ 0.01. Error bars depict ±SEM. D, E, Representative images (D) and graphs (E) depict quantification of the percentage and the relative fold change of Smo-localization in the primary cilia of DIV3 Smo-EGFP-electorporated primary GCPs culture 24 h post-treated with DMSO and SAG, respectively. Quantifications show three independent experiments. Statistical significance, one-way AVONA, Bonferroni's multiple comparison test; ***p ≤ 0.0001, **p ≤ 0.01. Error bars depict ±SEM. F, Schematic illustration of proposed model. Top, Hh signaling in the presence of Rab23. Rab23 inhibits Gli1 expression intracellularly at basal level. Rab23 also promotes the maintenance of primary cilium on granule cell progenitor. Upon Shh ligand stimulation on the primary cilium, Smo translocates to cilia axoneme, Gli1 expression increased, and Hh signaling is elevated. Bottom, In the absence of Rab23, Smo is enriched in cilia axoneme, Gli1 expression is upregulated independent of Shh ligand stimulation. The primary cilium formation and/or maintenance are compromised, the GCP is not responsive to Shh ligand stimulation from the cell surface (paracrine signaling). Ligand-induced Smo-enrichment in cilia axoneme is not triggered.
