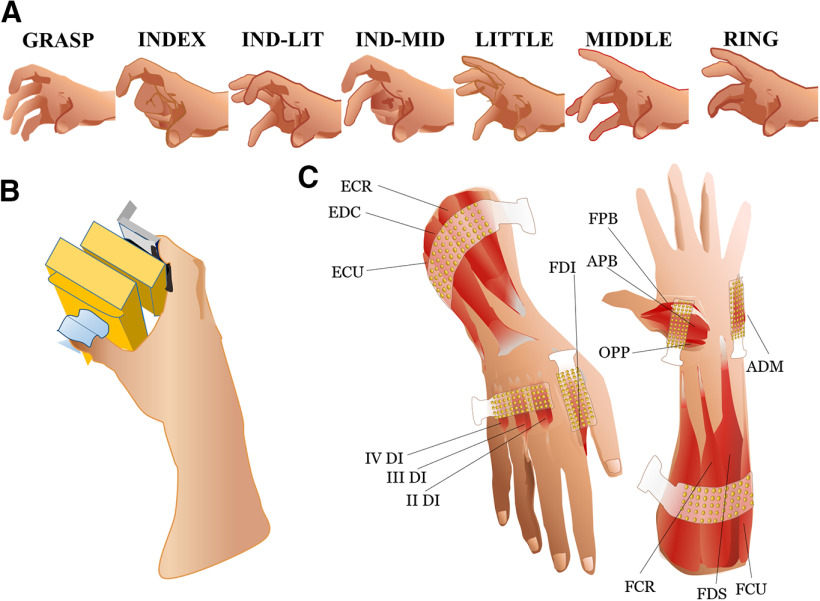
Figure 1.
Experimental setup and grip types. A, Subjects exerted sinusoidal isometric forces using seven grip types: all digits (GRASP), thumb in opposition to the index and middle fingers (IND-MID), index and little fingers (IND-LIT), and thumb in opposition to each finger in isolation (INDEX, MIDDLE, RING, and LITTLE, respectively). B, Hand posture grasping the sensorized grip device used for the experiment. C, Electrode placement for HD-sEMG recordings using six 13 × 5-electrode grids (total of 384 channels). Two larger grids (8-mm IED) were placed over the extensor and flexor extrinsic muscles of the hand. The grid on the dorsal side of the forearm was positioned to detect EMG signals from the ECU, the EDC, and the ECR muscles. The grid on the volar side of the forearm was positioned to detect EMG signals from the FCU, the flexor FDS and the FCR muscles. The four smaller grids (4-mm IED) were placed over the FDI, the other three dorsal interossei (II–IV DI), the ADM muscles, and the three thenar muscles: OPP, FPB, and APB.