Figure 3:
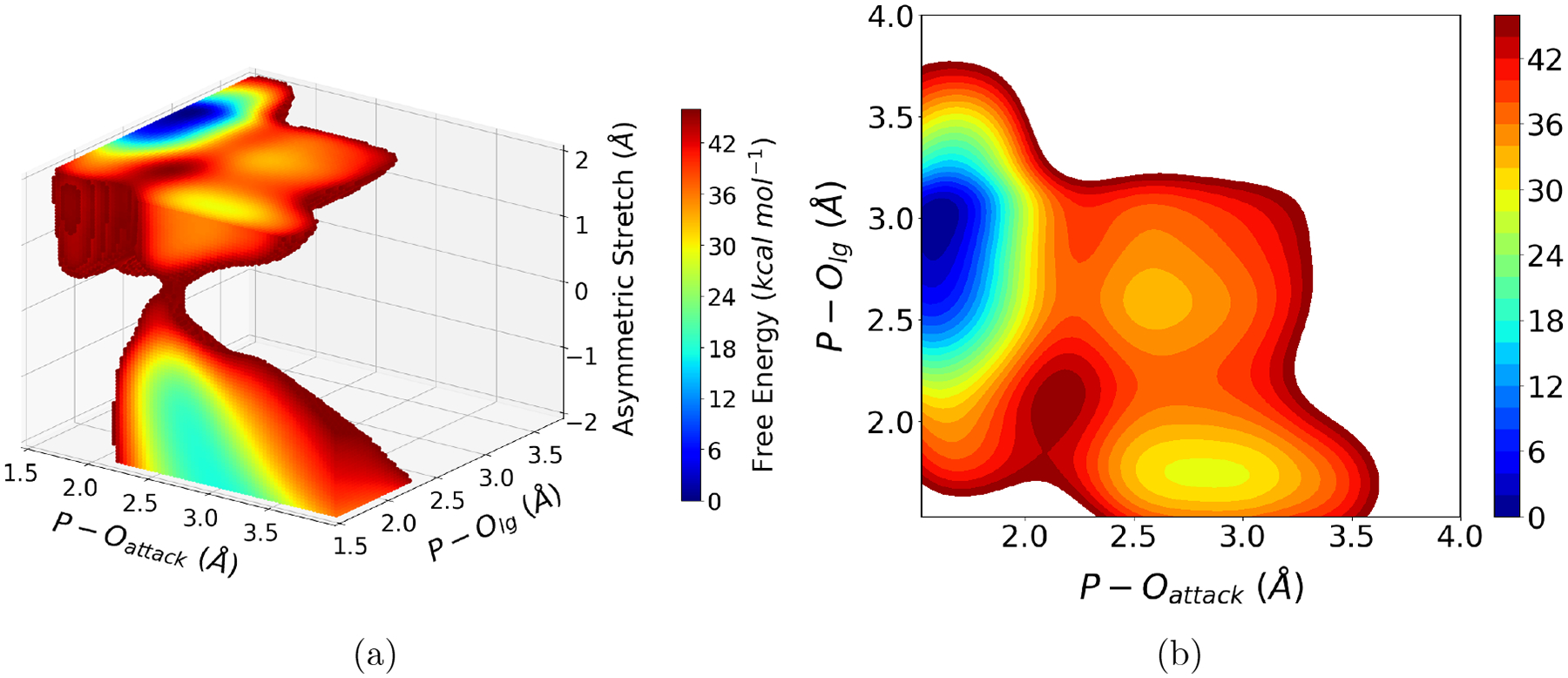
Results from an automated reinforcement learning driven free energy simulation of methyl phosphate hydrolysis in solution. The three coordinates are the nucleophilic attack P-O distance, the leaving group P-O distance and the antisymmetric O-H-O stretch that describes the proton transfer from the nucleophile (water) to the phosphate oxygen. (a) The three-dimensional PMF converges after 42 iterations of automated restrained MD-reinforcement learning cycles; the results indicate that with the current DFTB3/MM model, the solvent-assisted pathway120 is not the dominant mechanism. (b) The two-dimensional PMF cut after the proton transfer is complete indicates a dissociative pathway that involves a loosely bound metaphosphate species. Further refinement of the QM/MM energetics will provide insights into this prototypical phosphoryl transfer reaction at an unprecedented level of detail.
