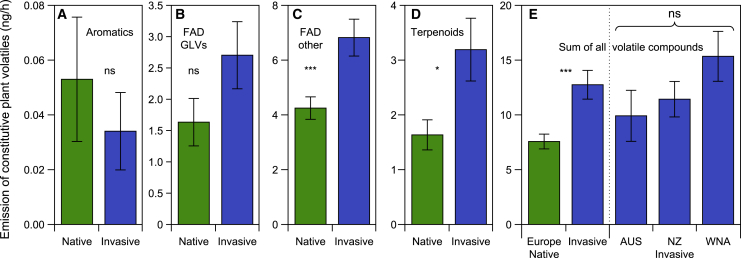
Figure 3.
Constitutive plant volatiles (CPVs) emission by native and invasive Jacobaea vulgaris genotypes
(A–D) Total emission of CPVs from different metabolic pathways: aromatic compounds (A); fatty-acid-derived (FAD) green leave volatiles (GLVs) (B); other FADs (C); and terpenoids (D). This comparison of VOC groups emitted by invasive and native Jacobaea vulgaris genotypes is based on the volatiles collected during the moth olfactometer test. Values are means ± SE. Linear mixed models (LMMs): (A) χ2(1) = 0.531, p = 0.47; (B) χ2(1) = 2.654, p = 0.10; (C) χ2(1) = 14.752, p < 0.001; (D) χ2(1) = 6.001, p = 0.014. This classification of VOCs is based on the most common metabolic pathways used by plants to produce volatile compounds. Asterisks indicate significant differences between origin; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ns, not significant.
(E) Total leaf volatile emission of invasive and native J. vulgaris genotypes originating from different ranges used in the moth olfactometer experiment. Values are means ± SE (n = 10 for AUS, n = 10 for NZ, n = 16 for WNA, and n = 36 for Europe). LMM, origin: χ2(1) = 13.257, p < 0.001; range within origin: χ2(2) = 5.409, p = 0.067. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ns above the three invasive ranges represents no significant difference among the three invasive ranges.