Figure 1.
LBD3 and LBD4 are cytokinin primary response genes
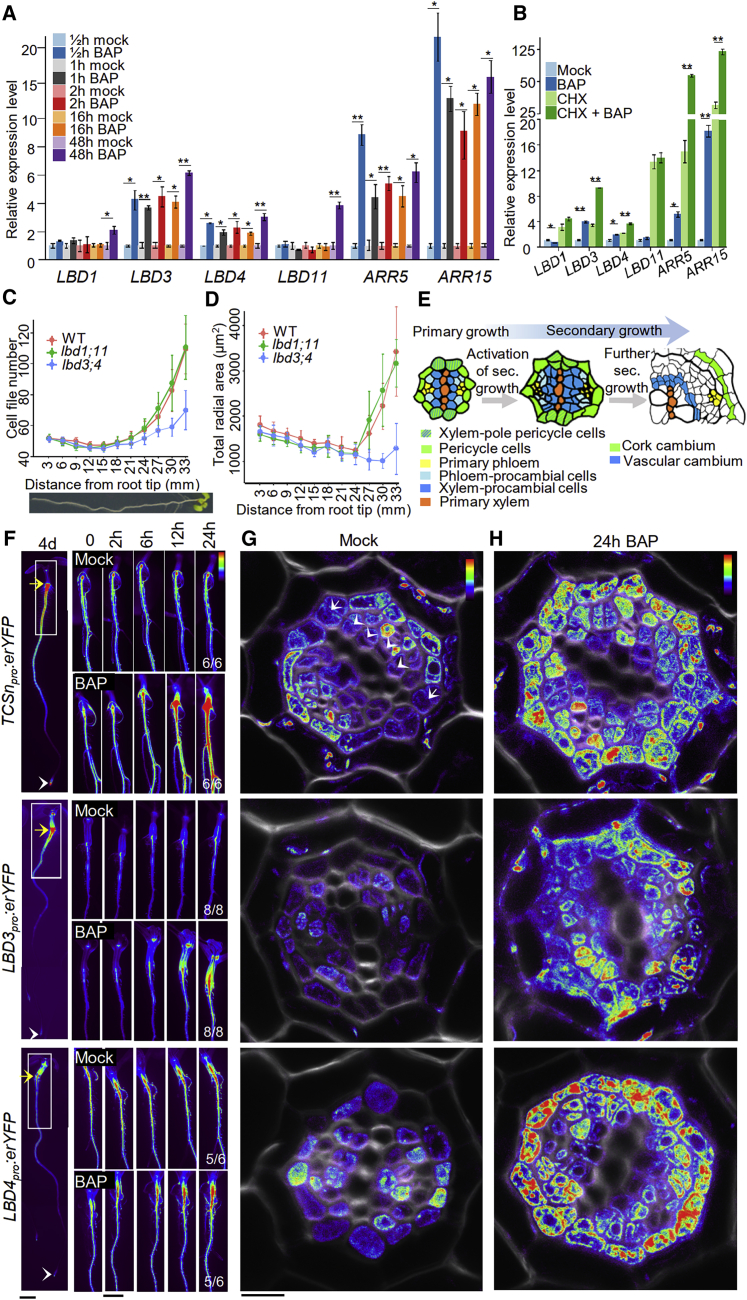
(A) qRT-PCR analysis of gene transcription after a time course of BAP treatment in 5-day-old roots.
(B) qRT-PCR analysis of gene transcription in 5-day-old plants (whole plants) after mock or BAP treatment in the absence or presence of cycloheximide (CHX).
(C and D) Cell file number (C) and total radial area (D) of pericycle and procambium lineage of 7-day-old roots were quantified (data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 7–31). See Figure S2A for details. Roots were cross-sectioned in 3 mm intervals. x axis indicates the distance of cross-sections from root tip.
(E) Schematic illustration of the developmental progression of root primary vascular tissue into secondary vascular tissue. Adopted from Smetana et al.17
(F) Stereo microscopy of fluorescent reporter lines of 4-day-old (left panel) and 6-day-old (right panels) roots. Time course visualization after BAP or mock treatment (right panels). Numbers represent the frequency of the observed expression in independent roots. Yellow arrows indicate the root-hypocotyl junction. White arrowheads mark root tips. White boxes approximately represent the corresponding region visualized in the right panels.
(G and H) Confocal microscopy (heatmap) of TCSnpro:erYFP, LBD3pro:erYFP and LBD4pro:erYFP root cross-sections. 6-day-old plants were treated for 24 h with mock (G) or 1 μM BAP (H). Sections were collected from the region undergoing activation of secondary growth (~1.5 cm below the root-hypocotyl junction). Arrowheads and arrows indicate cell divisions in the procambium and pericycle, respectively (G).
Data are presented as mean ± SE from three biological replicates in (A) and (B). Two-tailed t test. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01. Scale bars, 1 mm (F) and 10 μm (G and H). See also Figures S1 and S2A.