Figure 3.
Early antigen-specific CD4+ helper T cell responses shape humoral and cellular adaptive immune responses to mRNA vaccination
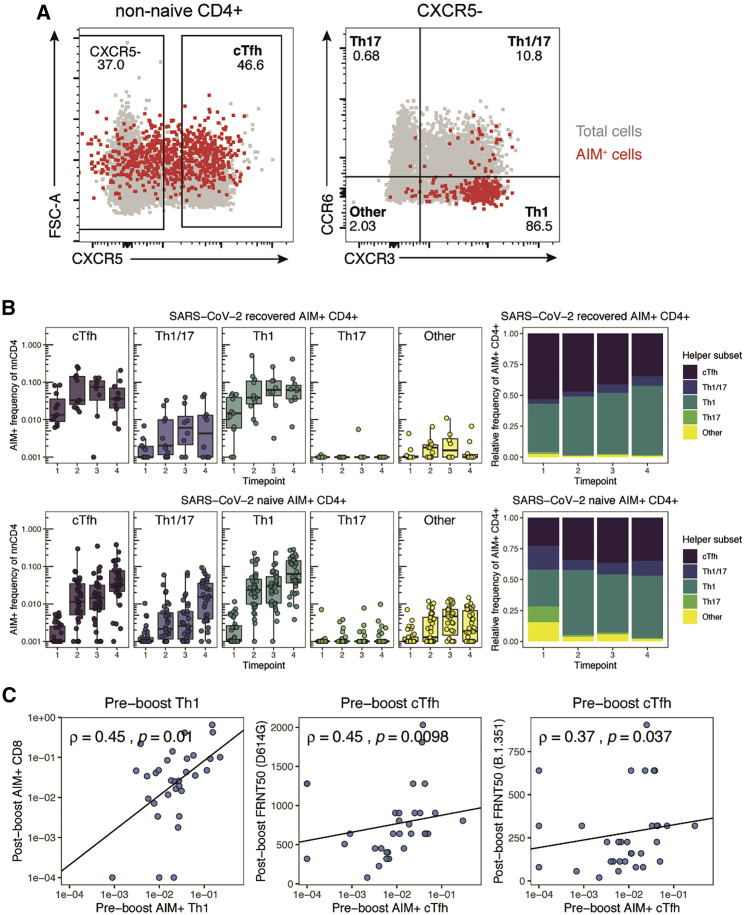
(A) Representative flow cytometric plots depicting the gating of AIM+ (CD200+CD40L+) CD4+ T cells to identify the indicated helper subsets in a SARS-CoV-2-naive donor at time point 4. Red events depict AIM+ T cells, gray events depict total CD4+ T cells from the same donor.
(B) Frequency of T helper subsets in AIM+ CD4+ T cells. Top panel depicts SARS-CoV-2-recovered donors. Bottom panel depicts SARS-CoV-2-naive donors. Left panel depicts the background-subtracted percentage of non-naive CD4+ T cells that are AIM+ helper T cells in each subset. Right panel depicts the relative frequency of each helper T cell subset in the background-subtracted AIM+ population. cTfh, CXCR5+ of non-naive CD4+ T cells; Th1, CXCR5− CXCR3+ CCR6−; Th17, CXCR5− CXCR3− CCR6+; Th1/17, CXCR5− CXCR3+ CCR6+; Other, CXCR5− CXCR3− CCR6−. Boxplots represent median with interquartile range.
(C) Correlations between the frequency of pre-boost (time point 2) AIM+ Th1 or AIM+ cTfh cells with post-boost (time point 4) AIM+ CD8+ T cells or neutralizing titers against dominant (D614G) or variant (B.1.351) strains of SARS-CoV-2 as published in a previous study of the same cohort (Goel et al., 2021). FRNT50, focus reduction neutralization titer 50%. Only SARS-CoV-2-naive donors were considered for these correlations. Associations were calculated using Spearman rank correlation and are shown with Pearson trend lines for visualization. Time points are as defined in Figure 1A.
Longitudinal samples from 36 SARS-CoV-2-naive and 11 SARS-CoV-2-recovered individuals were used for each experiment, analyzed in nine independent batches. All paired longitudinal samples were analyzed within a single batch. See also Figure S3.