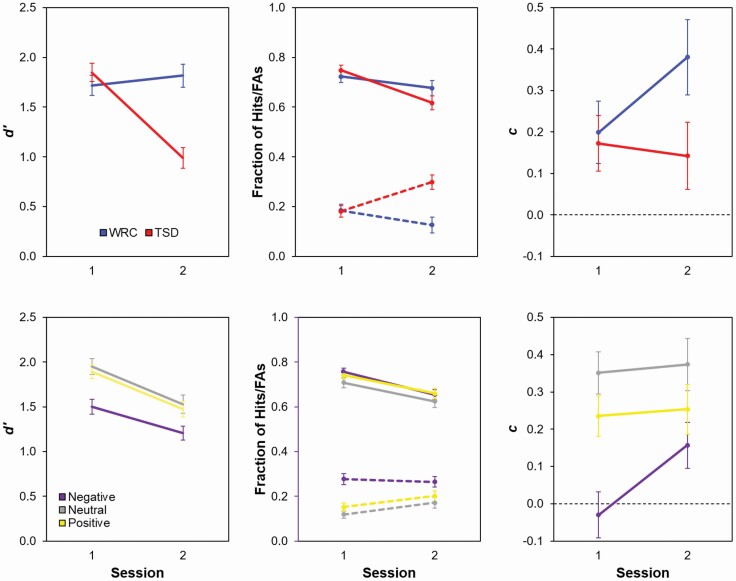
Figure 1.
Effects of sleep deprivation on item memory in the AISM task. The top panels show means (± SE) for discriminability (d’), hits (solid lines) and false alarms (FAs, dashed lines) as a proportion of total trials, and criterion (c) values across sessions 1 (baseline) and 2 as a function of study condition (TSD or WRC), collapsed across affective valence. The bottom panels show means (± SE) for d′, hits and FAs, and c across sessions as a function of affective valence, collapsed across condition.