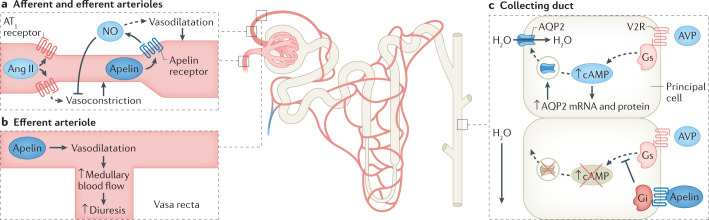
Fig. 4. The actions of apelin in the nephron.
a | Apelin acts at the afferent and efferent arterioles to promote vasodilatation via production of nitric oxide (NO), opposing the action of angiotensin II (Ang II). b | Increased vasodilatation at the efferent arteriole directly increases blood flow through the vasa recta, leading to increased medullary blood flow and promoting diuresis. c | The action of apelin counteracts vasopressin signalling in the kidney tubules. In the principal cells of the collecting duct, apelin prevents vasopressin-induced translocation of aquaporin 2 (AQP2) channels to the apical membrane and therefore prevents water reabsorption. AT1 receptor, type 1 angiotensin II receptor; AVP, arginine vasopressin; Gi, inhibitory G protein α-subunit; Gs, stimulatory G protein α-subunit; V2R, vasopressin v2 receptor.