Figure 4.
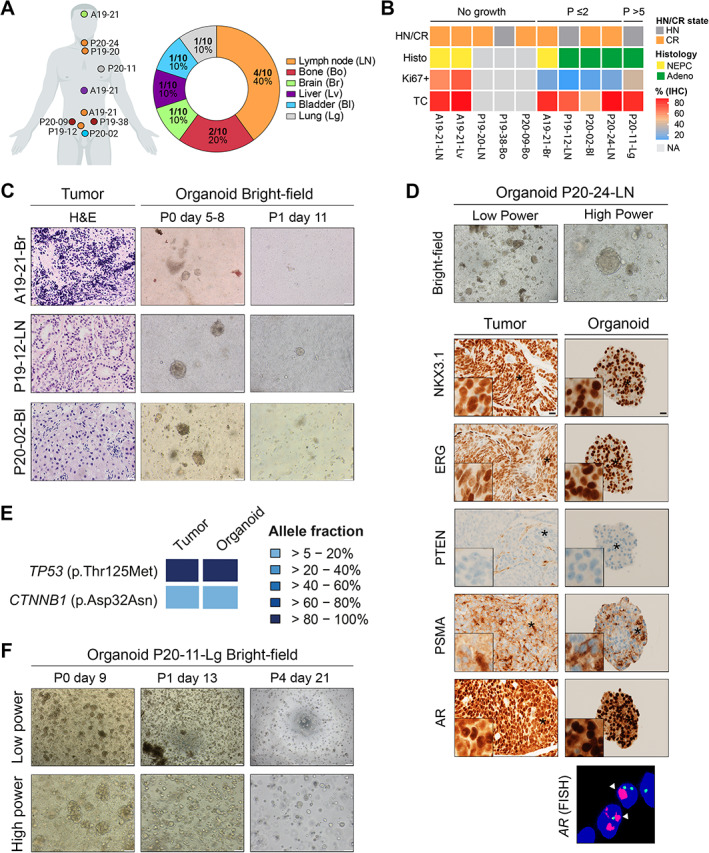
Organoids derived from metastasis specimens are established with poor efficiency and low stability. (A) Summary of tissue sites for advanced samples used to generate organoids (n = 9 metastasis and 1 local progression). Each patient code and its corresponding tissue site are indicated on the left schematic. Created in part with BioRender.com. (B) Heatmap depicting characteristics of samples separated into three groups of organoid growth: ‘No growth’; ‘P ≤ 2’: less than two passages; and ‘P > 5’: more than five passages. HN, hormone‐naïve; CR, castration‐resistant; NEPC, neuroendocrine prostate cancer; Adeno, adenocarcinoma; TC, tumor cells; NA, not available. (C) Examples of samples which initially grew in organoid culture but stopped after passaging. Representative H&E images of tumor samples and bright‐field images of their derived organoids at passage 0 (P0) and passage 1 (P1) are shown. Scale bars: 20 μm for H&E images, 100 μm for bright field images. (D) Morphological and molecular analyses of a lymph node metastasis sample (P20‐24‐LN) and its matched organoid line which stopped growing at passage 2. Bright‐field (BF) images and immunostaining for the indicated antibodies are presented (day 9). Insets show higher magnification of a representative region indicated by an asterisk. Right panel: FISH analysis using AR (red) and CEPX (green) probes. White arrowheads indicate AR amplification. Scale bars represent 200 and 100 μm for bright‐field images and 20 μm for IHC images. (E) Targeted sequencing identifies specific TP53 and CTNNB1 mutations in the P20‐24‐LN tumor sample and its derived organoid line. The heatmap indicates the variant allele fractions of the somatic mutations (blue, see color key). (F) Representative bright‐field images of the organoid line derived from a lung metastasis (P20‐11‐Lg) at passage 0 (P0) and later passages (P1: passage 1; P4: passage 4). Scale bars: 200 μm for low‐power images; 100 μm for high‐power images.
