Scheme 1.
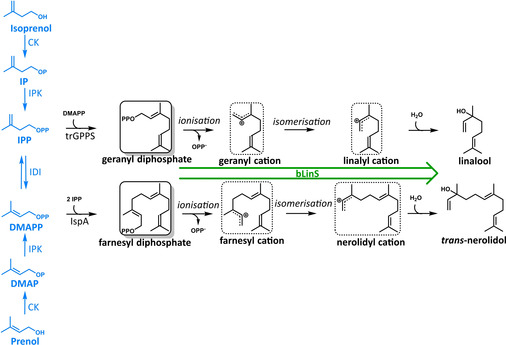
IU pathway and the proposed mechanism for the formation of linalool and trans‐nerolidol in the engineered E. coli strain using the GPPS‐bLinS module. Isoprenol and prenol are phosphorylated by choline kinase (CK) producing isopentenyl phosphate (IP) and dimethylallyl phosphate (DMAP), respectively. A second phosphorylation is catalysed by isopentenyl phosphate kinase (IPK), producing isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP), which are isomerized by isopentenyl diphosphate delta‐isomerase (IDI), shown in blue. The C5 isoprenoid precursors are converted to the mono‐ and sesquiterpenoid substrates geranyl diphosphate (GPP) and farnesyl diphosphate (FPP) by a heterologous truncated GPP synthase (trGPPS) and an endogenous FPP synthase (IspA) respectively. bLinS accepts both GPP and FPP which are converted to linalool and trans‐nerolidol, respectively. Carbocation reaction intermediates are highlighted with dashed boxes. The isomerisation steps occur via linalyl diphosphate and nerolidyl diphosphate.
