Figure 1.
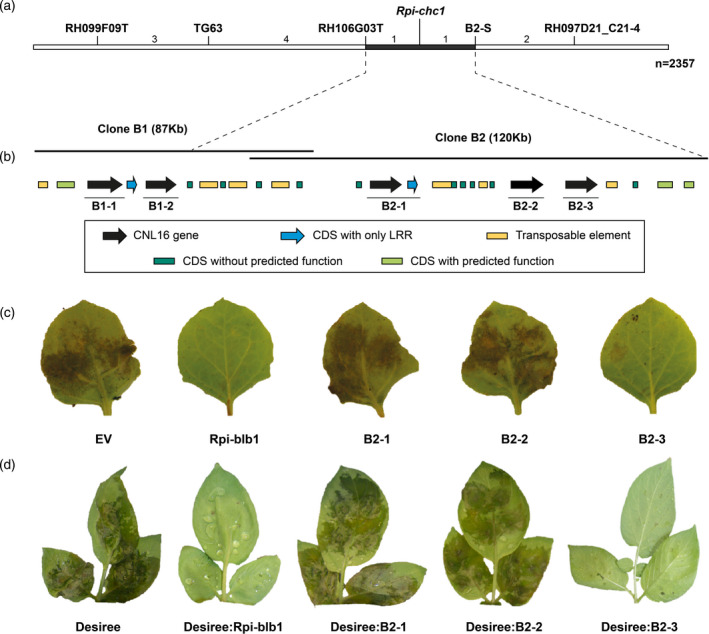
Map‐based cloning of Rpi‐chc1.1.
(a) Genetic map of P. infestans (isolate 90128) resistance from CHC543‐5. The number between the markers represents the number of recombinants found in a population derived from 2357 seedlings. Markers starting with RH were derived from BAC end sequences generated by PGSC. Marker B2‐S represents the BAC end marker from clone 2. The black horizontal line represents the interval of Rpi‐chc1.1. (b) Two BAC clones were isolated to generate the physical map. Annotation revealed the presence of NB‐LRR genes, genes with or without predicted function, and transposable elements. Three complete NB‐LRR (B2‐1, B2‐2, and B2‐3) genes between flanking markers RH106G03T and B2‐S were selected as candidates. (c) The three candidates were expressed through agroinfiltration in N. benthamiana leaves. An empty vector (EV) and Rpi‐blb1 were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. Only candidate B2‐3 was able to compromise the growth of P. infestans isolate 90128. (d) The three candidates were stably transformed into the potato variety Desiree. After inoculation with isolate 90128, only the candidate B2‐3 was able to provide resistance. Untransformed Desiree and Desiree plants stably transformed with Rpi‐blb1 were used as negative and positive controls, respectively.
