Fig. 1.
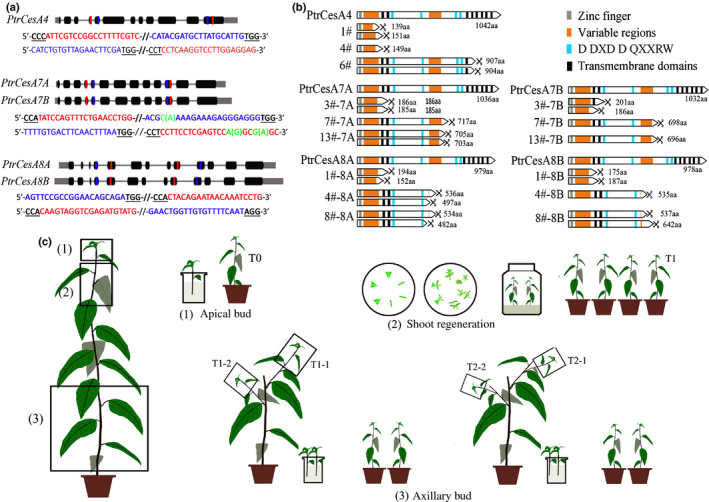
Cas9/gRNA‐induced mutations in PtrCesA4, PtrCesA7A/B, and PtrCesA8A/B genes of Populus trichocarpa (CesA, cellulose synthase). (a) Twelve gRNAs were designed in PtrCesA4, PtrCesA 7A /B and PtrCesA 8A /B genes. Nucleotides in blue and red represent the target sites. (b) The deduced amino acids of protein‐coding regions from the Cas9/gRNA‐edited genes in nine putative ptrcesa knockout mutants (ptrcesa4‐1#, −4# and − 6#, ptrcesa 7a /b‐3#, −7# and − 13#, ptrcesa 8a /b‐1#, −4# and − 8#). The scissors indicate protein‐coding termination. (c) Three asexual propagation methods (apical bud cloning, axillary bud cloning and shoot regeneration) were used to generate progeny from the ptrcesa mutants with the Cas9/gRNA‐induced mutations. The apical buds and axillary buds were rooted hydroponically and planted in soils.
