Fig 2.
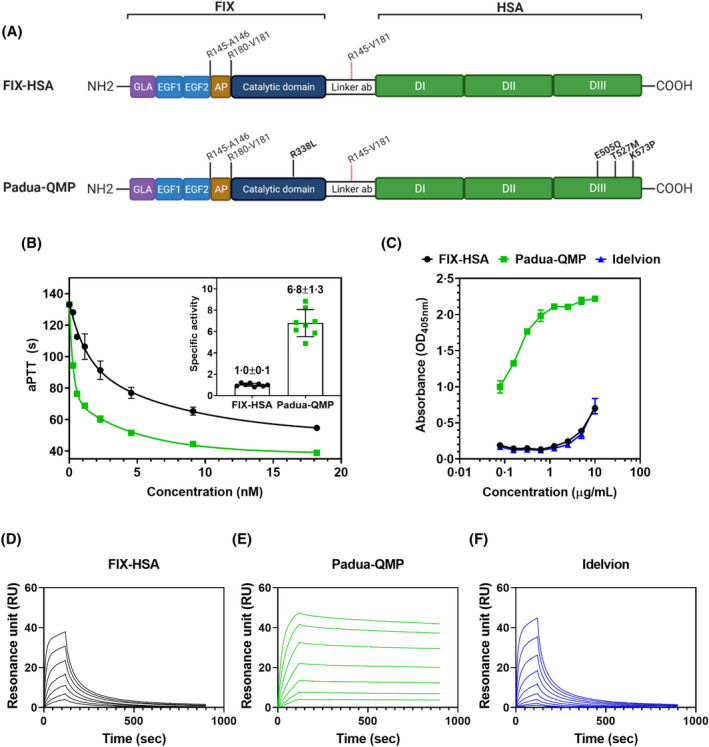
Engineering of the FIX‐HSA fusion improves procoagulant activity and hFcRn binding. (A) Schematic representation of the designed fusion proteins of FIX and HSA connected via the cleavable linker ab. FIX is activated by proteolytic cleavage at the two cleavage sites indicated (R145‐A146 and R180‐V181). Simultaneous detachment of HSA is accomplished as the linker sequence (linker ab) contains an upstream–downstream combination of the two cleavage sites in FIX (R145‐V181). FIX‐HSA consists of wild‐type FIX and wild‐type HSA (upper panel). Padua‐QMP contains point mutations in FIX (R338L, Padua) and HSA (E505Q/T527M/K573P) as indicated in bold. According to Human Gene Variation Society (HGVS) nomenclature,60 the corresponding positions/substitutions are R191‐A192/R226‐R227 (activation sites) and R384L (Padua variant) for FIX, and E529Q/T551M/K597P for the QMP variant. Created with Biorender.com. (B) Representative procoagulant activity of serial dilutions of purified fusion proteins, evaluated by aPTT‐based assays. The resulting specific activity is reported (inset). (C) Binding of titrated amounts of purified fusion proteins to immobilised hFcRn at pH 5·5. Results are reported as mean ± standard deviation of duplicates from one representative experiment. (D–F) Representative sensorgrams showing binding of serial dilutions (0–4 µM) of monomeric hFcRn injected over immobilised (~200 RU) fusion proteins at pH 5·5. AP, activation peptide; aPTT, activated partial thromboplastin time; DI, domain I; DII, domain II; DIII, domain III; EGF1 epidermal growth factor‐like domain 1, EGF2, epidermal growth factor‐like domain 2; FIX, factor IX; GLA, gamma‐carboxyglutamic acid domain; HSA, human serum albumin; hFcRn, human neonatal Fc receptor.
