Table 1.
Mechanisms of action and clinical studies of Allium sativum, ascorbic acid, curcumin, Nigella sativa, vitamin D, and Zingiber officitale in the management of COVID-19
| Medicinal Plants & Vitamins | Mechanisms of Action | Clinical Studies |
|---|---|---|
Allium Sativum (garlic)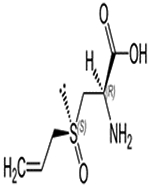
|
Garlic and its derivatives have potential antiviral activity against different human, animal, and plant pathogenic viruses through blocking viral entry into host cells, inhibiting viral RNA polymerase, reverse transcriptase, DNA synthesis and immediate-early gene 1(IEG1) transcription, and also through downregulation of the extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling path47. | Clinical studies demonstrated the prophylactic and chemo preventive effects of garlic against viral infections in humans’ through enhancing the immune response47. A clin A clinical trial showed that supplementation of aged garlic modulated the inflammation and immunity of adults with obesity108. |
Ascorbic acid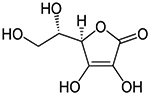
|
Ascorbic acid enhances the immune system by stimulating IFN production, lymphocyte proliferation, and enhancing the neutrophil phagocytic capability109. | A clinical trial demonstrated that vitamin C reduces pneumonia in lower respiratory tract infections. This clinical study suggest that vitamin C may work against SARS-CoV-2. |
Curcumin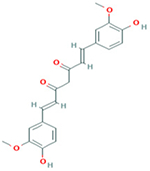
|
Curcumin has anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects by downregulating the expression of crucial chemokines and cytokines involved in lung infection such as INNy, MCP-1, IL-6110. Curcumin inhibits human respiratory syncytial virus infection by preventing RSV replication, release of TNF-alpha and downregulating phosphor-NF-kB111. | Clinical trials needed. |
Nigella Sativa
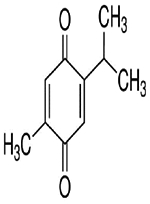
|
Two biologically active agents from N. sativa (nigellimine and thymoquinone) have the potential considered to treat COVID-19 patients65. | Clinical trials needed. |
Vitamin D
|
Immunomodulatory property72. Innate cellular immunity is strengthened by vitamin D actions directly or indirectly via antimicrobial peptides including human cathelicidin (LL-37), 1,25-dihdroxyvitamin, and defensins in a wide range of cell types including keratinocytes, epithelial cells, human monocytes and macrophages95. |
Clinical studies looking at the impact of vitamin D on COVID-19 found that people who have vitamin D deficiency were more likely to test positive for the virus that causes COVID-19 compared to people with normal levels of vitamin D90. |
Zingiber Officitale (Ginger)
|
The active components of ginger (6-gingerol) have been shown to be an effective antiviral against the COVID-19 virus due to its high binding affinity with multiple binding sites of the viral protein molecules107. | Clinical trials needed. |
