Figure 4: Characterization of an IL-4-elicited MCT phenotype enriched in diseased human lung samples.
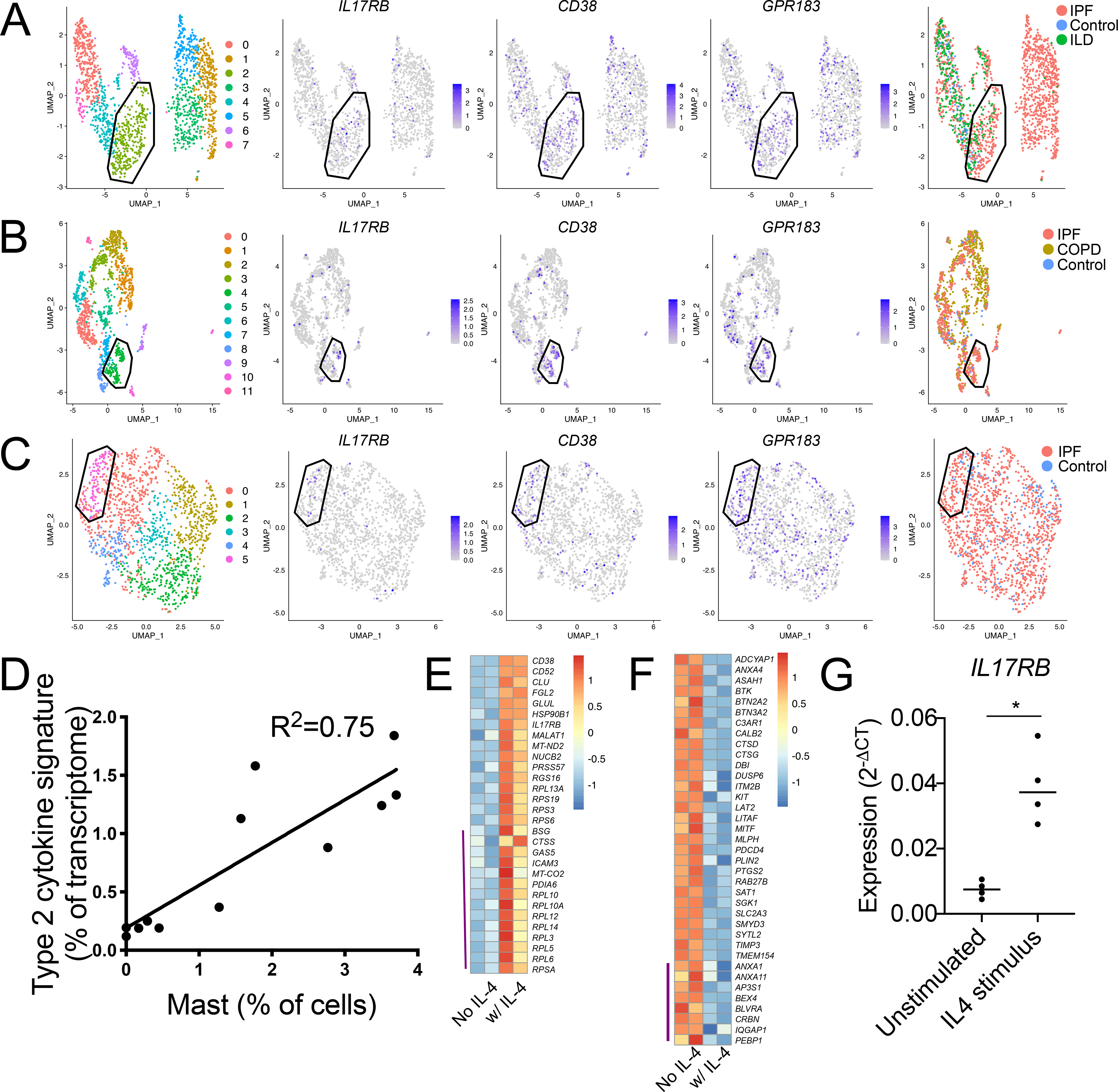
(A-C) Re-clustering of MCs from three scRNA-seq datasets accessed through the human IPF atlas: (A) control, IPF and ILD; (B) control, IPF and COPD; and (C) control and IPF. Clustering for each dataset indicated a population (polygon gate) that was statistically enriched for the polyp MC3-associated transcripts IL17RB, CD38, and GPR183 (center panels) and predominantly composed of MCs from diseased tissue relative to healthy (left panels). Circle gate indicates MCs co-expressing the proliferation-associated genes MKI67 and TOP2A.
(D) Correlation analysis of polyp scRNA-seq epithelial IL-4/13-induced signature expression, (donor averaged) versus scRNA-seq defined MC percentage for each donor. p<0.001.
(E) MC3-enriched transcripts (Supplementary table 4) upregulated in two technical replicate CBMC samples by 96-hour IL-4 stimulus (row normalized expression). Top half: FDR<0.1, bottom half (indicated by purple line): P < 0.05 (DESeq2).
(F) MC1-enriched transcripts (supplemental table 4) downregulated in two technical replicate CBMC samples by 96 hours IL-4 stimulus (row normalized expression). Top half: FDR<0.1, bottom half (indicated by purple line): P < 0.05 (DESeq2).
(G) CBMCs IL17RB expression (qPCR) following 72-hour stimulus with vehicle or IL-4, (n=4 biologic replicates across three independent experiments), * indicates p<0.05 (paired t-test).
