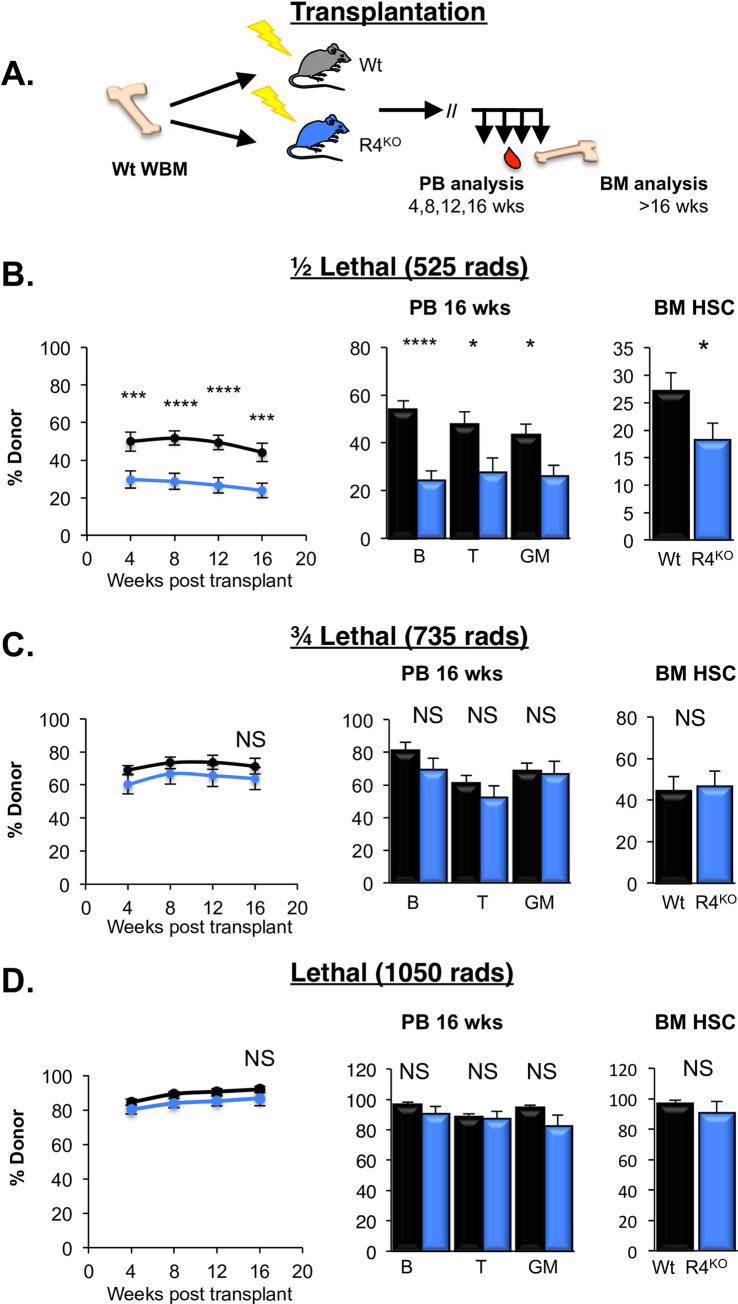
Fig 1. Requirement for vascular ROBO4 for efficient HSC engraftment can be overcome through increased radiation preconditioning.
A. Schematic of the transplantations into preconditioned recipients at 525, 735, or 1050 rads. B. Loss of Robo4 perturbed HSC reconstitution in R4KO recipients preconditioned with 525 rads compared to Wt recipients. Data represent total donor chimerism in the peripheral blood (PB) over time (line graph), and donor chimerism at the experiment endpoint (>16 wks post-transplantation) of B cells, T cells, and GM cells in the PB and HSCs in the bone marrow (BM). Black bars represent Wt and blue represent R4KO. n = 3 independent experiments per radiation dose with n = 21 Wt and n = 21 R4KO. We have previously published similar results at this dose [17]; this panel include new data at 525 rads performed side-by-side with the two doses below. Statistics: Unpaired two tailed student’s t-test. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.005 and **** p < 0.001. C, D. Increased radiation pre-conditioning resulted in no difference between R4KO and Wt host engraftment potential. Significant engraftment differences between R4KO and Wt recipients was absent with increased radiation pre-conditioning with both ¾ lethal dose (735 rads; C) or a lethal preconditioning dose (1050 rads; D) resulted in HSC reconstitution in R4KO hosts equivalent to that of Wt hosts. Data panels in C and D are organized as in panel B. Mice in B and C were transplanted with 7.5M WBM (equivalent to ~500 HSC) and mice in D were transplanted with 1.5M WBM GFP+ cells (~100 HSC). n = 3 independent experiments per radiation dose with n = 14 Wt (C), n = 12 R4KO (C), n = 15 Wt (D) and n = 14 R4KO (D). Statistics: Unpaired two-tailed student’s t-test. NS, not significant. See also S1 Fig.