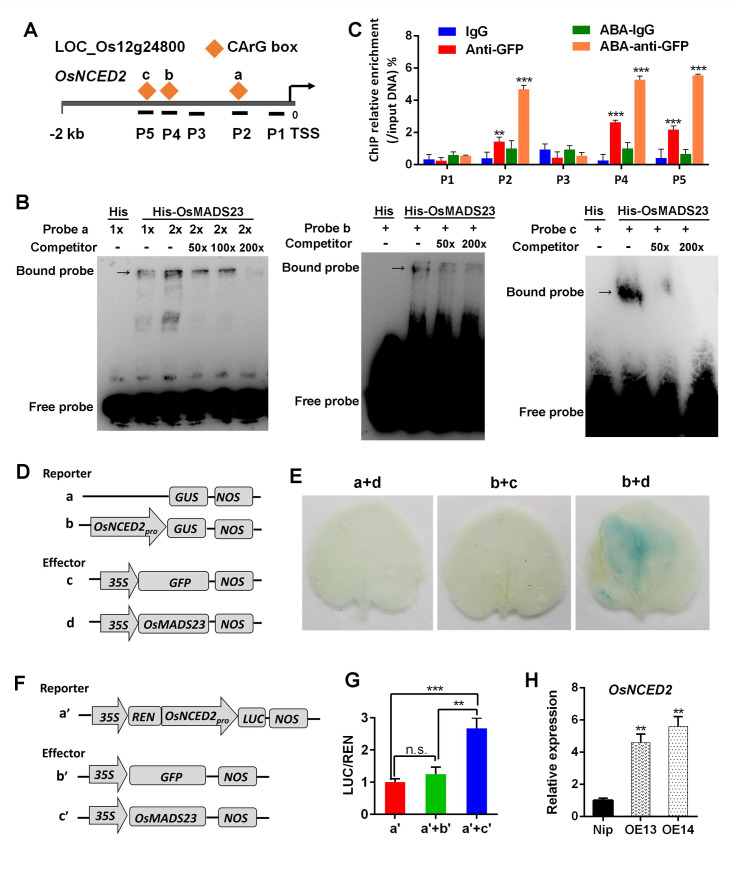
Fig 6. OsMADS23 is a transcriptional activator of OsNCED2.
(A) Schematic diagram of OsNCED2 promoter region showing the positions of CArG-box motifs and P1-P5 fragments amplified by ChIP-qPCR. (B) Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) indicating OsMADS23 binds the CArG-box motifs in OsNCED2 promoter specifically. Probe 1 (-1266 to -1226 bp), probe 2 (-1051 to -1010 bp) and probe 3 (-687 to -645 bp). (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation-quantitative PCR (ChIP-qPCR) assay showed that ABA enhances OsMADS23 binding to the promoter regions of OsNCED2. P1-P5 represents the regions shown in (A) detected by ChIP-qPCR. The enrichment values were normalized to input. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) immunoprecipitated DNA was used as a control. Error bars indicate SD with biological triplicates. Ten-day-old rice plants overexpressing OsMADS23-GFP were treated by ABA for 16 h and used for ChIP analysis. Error bars indicate SD with biological triplicates. (D) Schematic diagrams of the effector and reporter used for transient transactivation assays in the leaves of Nicotiana benthamiana. The fragment from -1362 to -574 bp in the promoter of OsNCED2 was used for constructing reporter. (E) Transactivation activity was detected by GUS staining in N. benthamiana leaves. (F) Schematic diagrams of the effector and reporter used for transient transactivation assays in rice protoplasts. REN, Renilla luciferase; LUC, firefly luciferase. The fragment from -1362 to -574 bp in the promoter of OsNCED2 was used for construction reporter. (G) Transactivation activity reflected by LUC activity of LUC/REN ratio. Data represent the means of three independent experiments. (H) Relative transcription levels of OsNCED2 in wild type (Nip) and OsMADS23-overexpressing plants. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 or ***p < 0.001 (Student’s t test). Three independent experiments were performed.