Fig. 1. PROMPT platform design and operation.
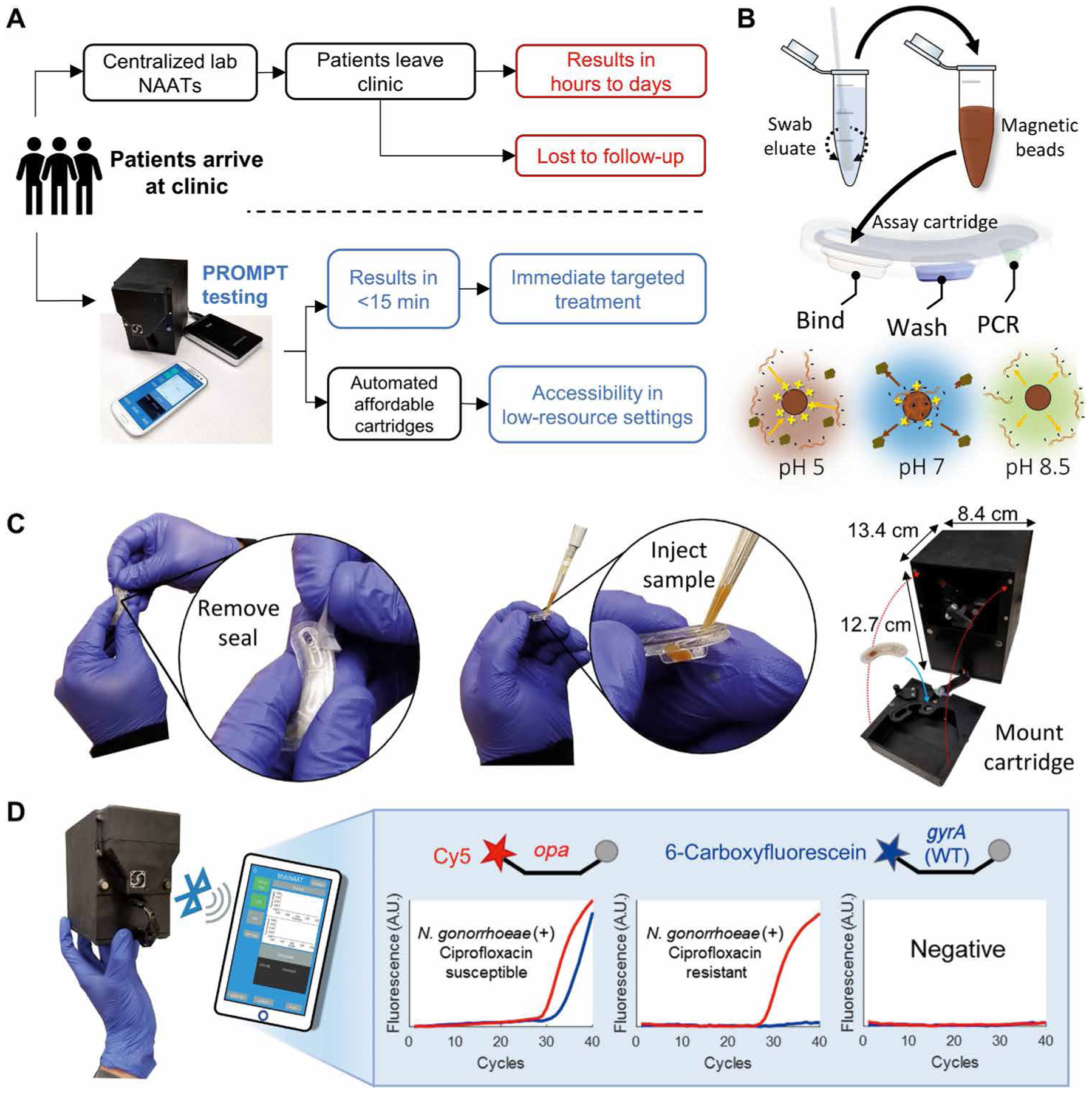
(A) Comparison of standard of care for N. gonorrhoeae diagnosis (top) versus proposed clinical workflow with the PROMPT platform (bottom). (B) Schematic shows processing of patient swab samples. Steps include swab elution, mixing eluate with magnetic beads, and injection into the assay cartridge, followed by pH-mediated automation of nucleic acid binding, purification, and elution using transfer of the beads through cartridge wells containing preloaded buffers. (C) Photographs of the PROMPT assay cartridge. Cartridges are sealed before use with an adhesive tape, which is removed before injection of the sample into the first well. The instrument’s faceplate detaches for loading the cartridge onto the PCR heat block. Remounting the faceplate with magnetic clasps aligns the cartridge with the instrument’s magnet arm and fluorescence detector. (D) Photograph and schematic showing the instrument interfacing with a smartphone or tablet using Bluetooth for real-time reporting of PCR amplification. PCR was used to determine whether N. gonorrhoeae was present in the clinical sample by opa amplification in the Cy5 channel (red) and whether the bacterial strain was susceptible to ciprofloxacin by wild-type (WT) gyrA amplification in the 6-carboxyfluorescein channel (blue). A.U., arbitrary units.
