Fig. 4. Clinical validation of the PROMPT platform.
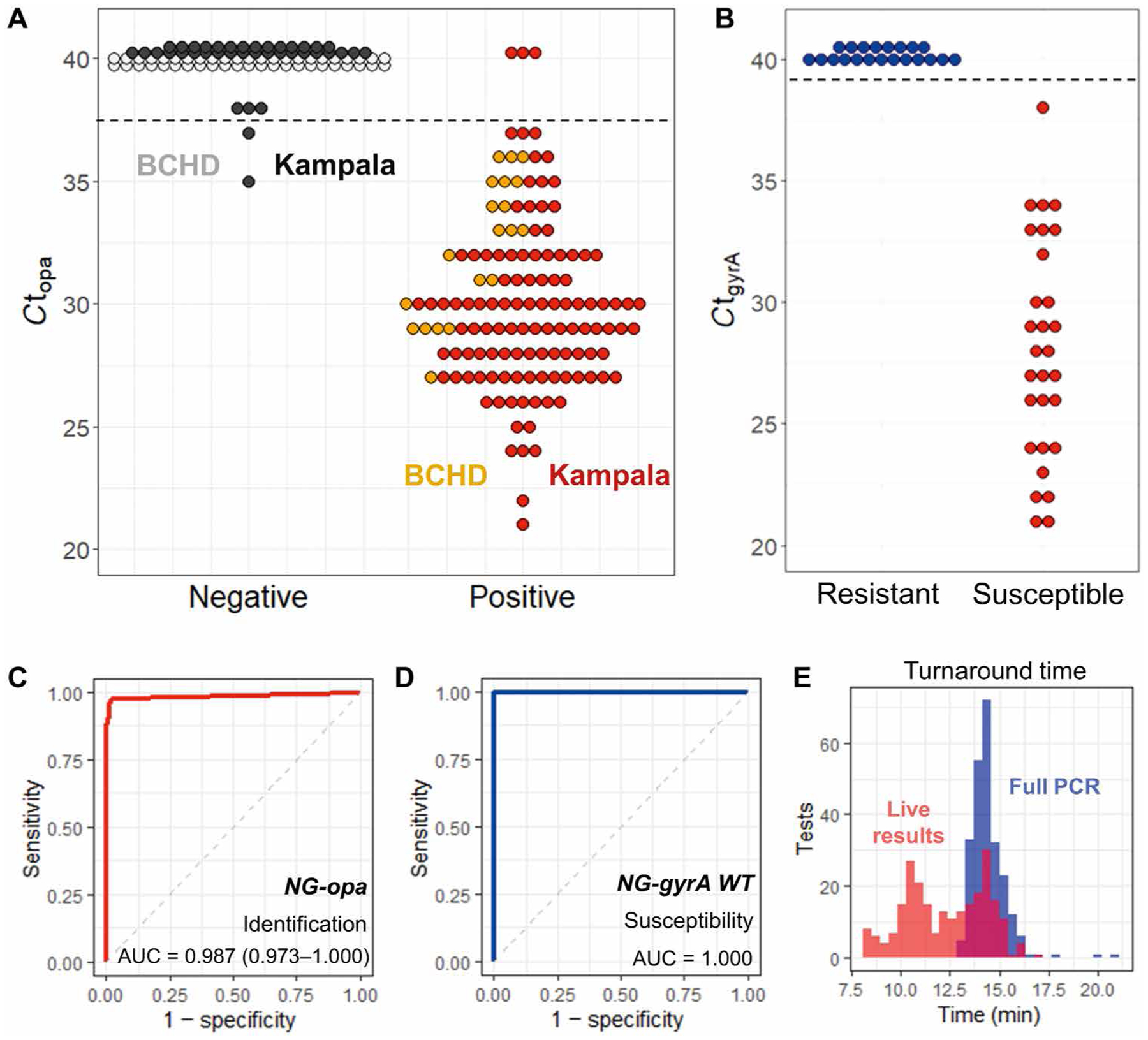
(A) Results of N. gonorrhoeae detection by the PROMPT cartridge assay show opa amplification cycle threshold (Ct) for BCHD swabs (n = 66) and swabs collected in Kampala, Uganda (n = 151). Samples with no amplification in this plot are given a Ct set at 40 (gray, black). Horizontal dashed lines indicate cutoff Ct values used to determine positive amplification by the PROMPT cartridge assay. (B) Ciprofloxacin susceptibility of N. gonorrhoeae in BCHD samples was predicted by amplification of wild-type gyrA and is compared to culture results for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. (C) ROC curve for N. gonorrhoeae (NG) identification by opa amplification in all swab samples. (D) ROC curve for N. gonorrhoeae ciprofloxacin susceptibility by gyrA amplification. (E) Turnaround times for all swab samples using the complete 40-cycle PCR (blue) or determined by the live-reporting algorithm for opa gene amplification (red).
