Figure 1. Noninvasive Brain Stimulation Techniques.
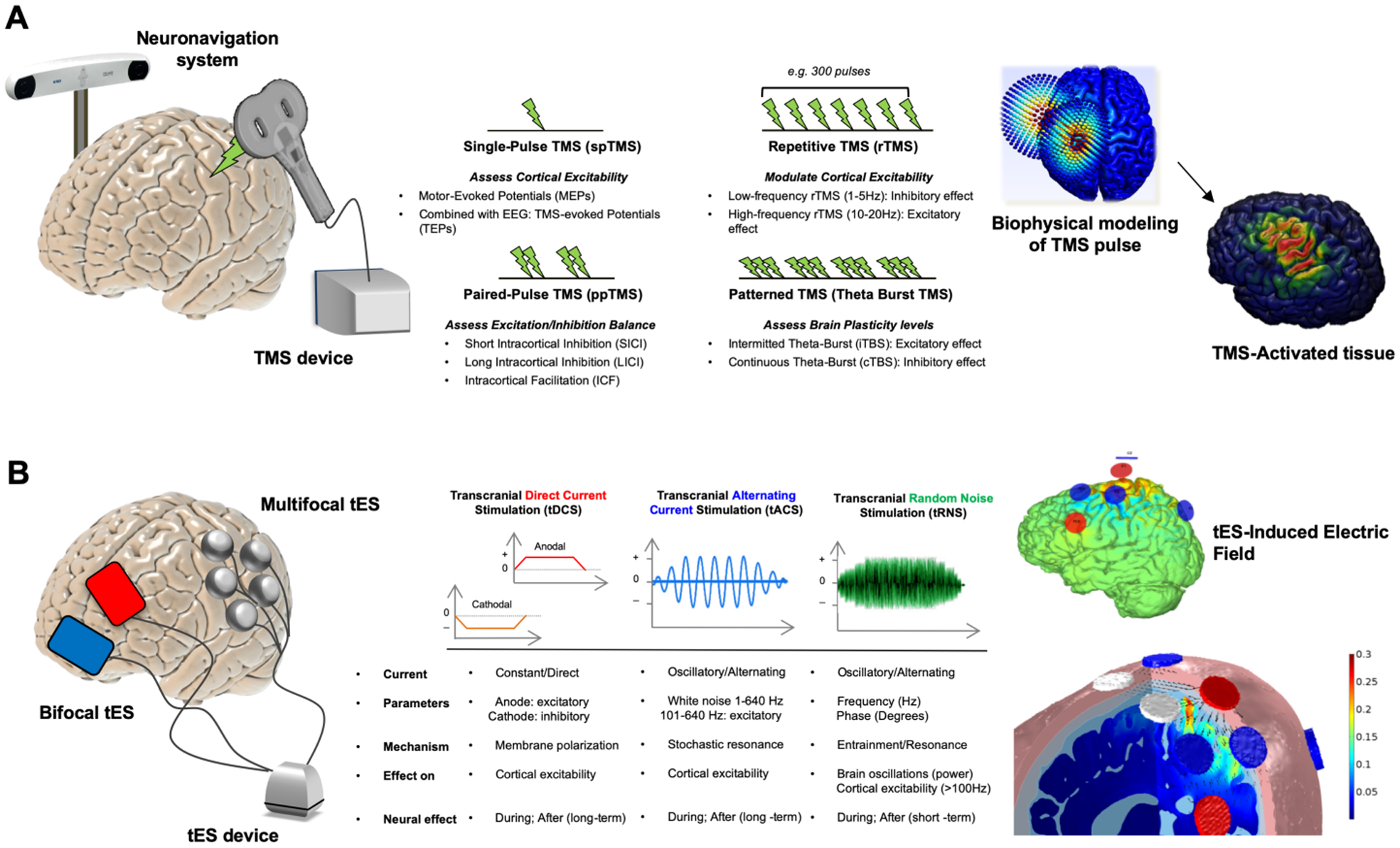
Panel A represents Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS). The coil induces a strong magnetic field exciting or inhibiting cortical activity (left). Different protocols can be implemented pairing more pulses with various effects (right). In panel B. we show the Transcranial Electrical Stimulation (tES). tES consists, at minimum, of two electrodes (red anode, blue cathode) applied directly on the scalp (left). More channels can be added to extensively record EEG or modulate brain activity via so-called multifocal/multielectrode protocols (Ruffini et al., 2013). Protocols include anodal (positive) and cathodal (negative) transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS), and transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS). Stimulation protocols differ from one another on various parameters including frequency of stimulation and induction of after-effects (right).
