Fig. 6.
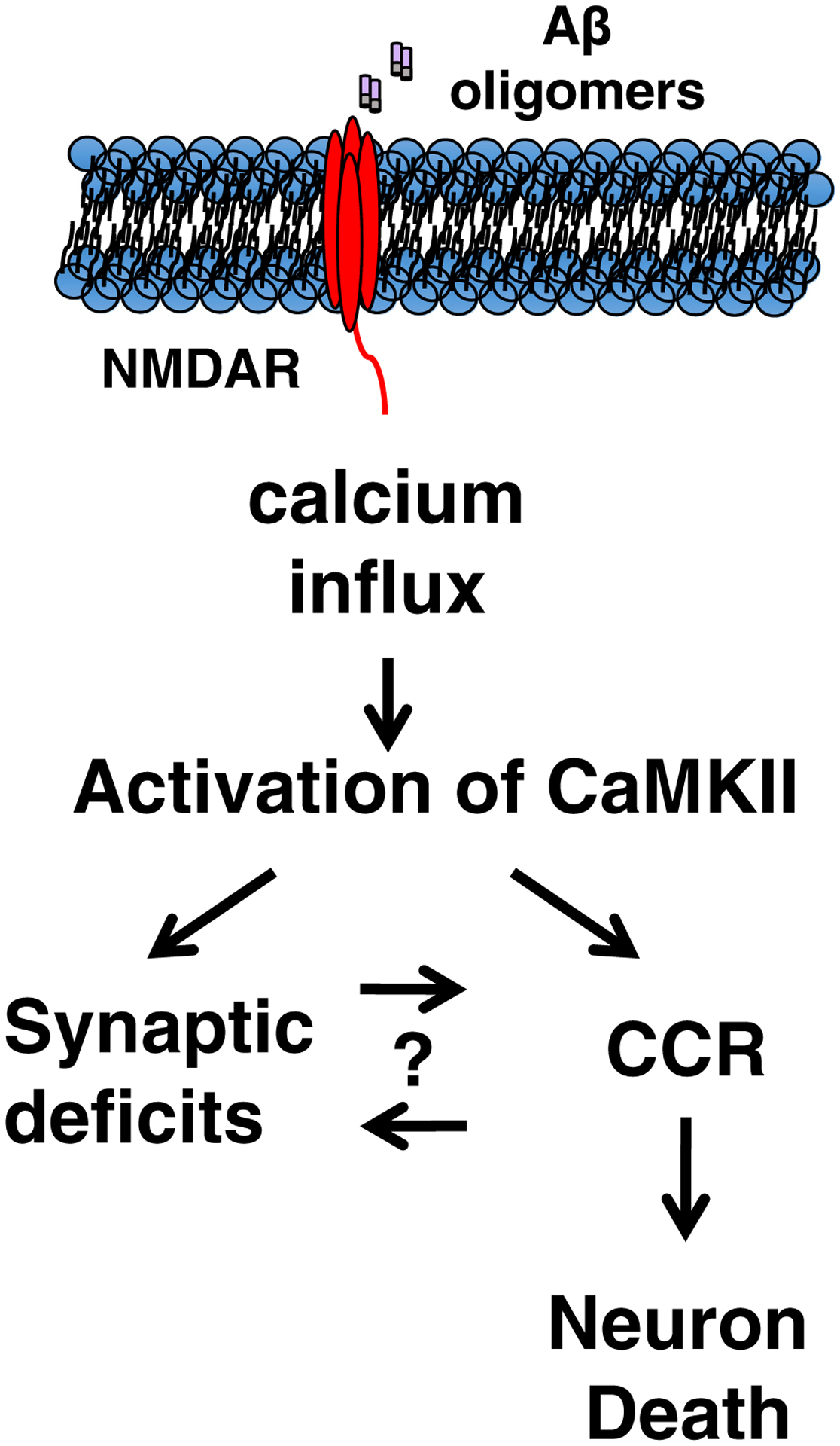
AβO-induced calcium influx via NMDAR is necessary for neuronal CCR. AβO-induced excitotoxicity contributes to many neuronal dysfunctions in AD, including synaptic deficits. Here, we show that AβO-mediated calcium influx via NMDAR is also necessary for initiating CCR. AβO-mediated synaptic dysfunction involving NMDAR could be initiating neuronal CCR directly, or alternatively, these pathways could diverge after AβO-mediated calcium influx, each contributing to neuron death independently. These two schemes are not necessarily mutually exclusive. Abbreviations: AβO, amyloid-β oligomer; AD, Alzheimer’s disease; CCR, cell cycle reentry; NMDAR, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor.
